What is a Digital Signature Certificate?
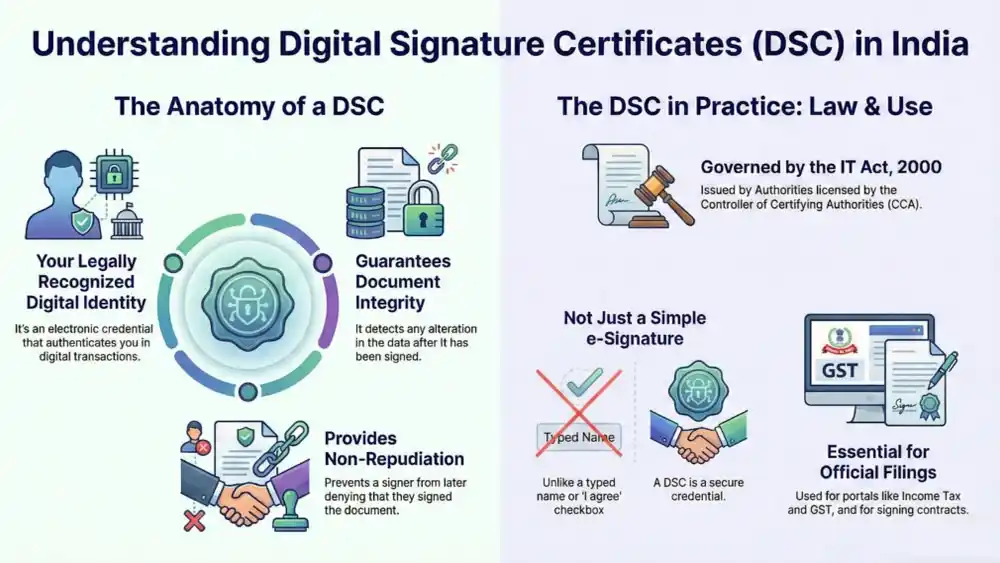
A Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) is a legally recognised electronic credential used to authenticate the identity of a person or entity in digital transactions. In India, a DSC enables secure electronic signing of documents and validates the signer’s identity through cryptographic technology under statutory law.
Definition
A Digital Signature Certificate is an electronic certificate that binds the identity of the holder with a pair of cryptographic keys. It is issued by a licensed Certifying Authority and is used to create a digital signature that ensures authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation of electronic records.
Key Characteristics / Features
- Issued only by a licensed Certifying Authority recognised under Indian law
- Based on asymmetric cryptography using a private key and a public key
- Confirms the identity of the signer in electronic records
- Ensures integrity by detecting any alteration in signed data
- Provides non-repudiation, preventing denial of having signed
- Legally equivalent to a handwritten signature for notified purposes
- Typically stored on a secure cryptographic device or token
Legal Recognition / Statutory Basis
Digital Signature Certificates are legally recognised under the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- Section 2(1)(p) defines a digital signature based on asymmetric crypto systems and hash functions.
- Section 3 provides legal recognition to digital signatures used for authenticating electronic records.
- Section 35 governs the issuance of Digital Signature Certificates by licensed Certifying Authorities.
The regulatory oversight and licensing of Certifying Authorities is administered by the Controller of Certifying Authorities (CCA), operating under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
What It Is and What It Is Not
What it is:
A Digital Signature Certificate is a specific, cryptography-based electronic authentication mechanism recognised under the IT Act. It is issued only after identity verification and is legally enforceable for notified electronic filings and documents.
What it is not:
It is not the same as a simple electronic signature, such as typing a name or clicking “I agree.” It is also distinct from Aadhaar-based eSign, which uses a different authentication framework, though both are electronic signatures under Indian law.
Common Use Cases
- Authentication of filings on government portals such as MCA, Income Tax, and GST systems
- Digital signing of statutory returns, forms, and compliance documents
- Secure execution of contracts and authorisations in electronic form
- Identity validation in regulated digital workflows
- Corporate and professional compliance submissions
