18,000+ Happy Customers
GST Registration Online 3-Day Approval (Rule 14A)
Get your GST Registration approved in just three working days under the new Simplified Scheme (Rule 14A) for eligible low-risk applicants. We manage the complete application, eligibility checks, & Aadhaar Authentication.


Request a Call Back
Timeline for GST Registration
While the initial filing is quick, the entire registration process typically takes 8-12 months due to statutory opposition periods and registry processing.
Filing &
Scheme Selection
We file Form GST REG-01 (Part A & B). If eligible (monthly B2B tax < ₹2.5L), we select the "Opt for Rule 14A" checkbox for fast-track processing.
Aadhaar
Validation
The Authorised Signatory completes OTP-based Aadhaar authentication. For high-risk cases, a mandatory visit to a GST Suvidha Kendra (GSK) for biometric verification is required.
Auto-Approval
(Rule 9A)
For low-risk applicants identified by the system (including eligible Rule 14A cases), the registration is deemed approved electronically within three working days.
Standard
Processing
For regular applications or high-risk cases requiring officer scrutiny/site verification, approval takes 7 to 30 days. Upon approval, Form REG-06 (GSTIN) is issued.
Overview of GST Registration in India
GST Registration is the statutory process of obtaining a unique 15-digit Goods and Services Tax Identification Number (GSTIN) from the Central Government. It is mandatory for businesses exceeding specified turnover thresholds under Section 22 of the CGST Act, 2017.
The government introduced the Simplified Registration Scheme (Rule 14A) effective from 1st November 2025. This fast-track route enables eligible low-risk small businesses to receive auto-approval within three working days through Aadhaar-based electronic verifications.

Pradeep Vallat
Founder "Niflr & Clyra"
"Setindiabiz’s knowledgeable, disciplined, and organized team made our company registration, tax, and IPR filings smooth, hassle-free, and worry-free. 👍"
Setindiabiz is Trusted By Leading Brands































Pricing & Packages for GST Registration
- Eligibility & Category Check
- Prepare GST REG-01 Form
- File Application on GST Portal
- ARN Generation & Tracking
- Query Support (if raised)
- GSTIN / REG-06 Certificate
- Portal Login Handover
- GST return filing (GSTR-1/3B)
- DSC procurement / DSC token
- Notice reply/hearing support
- Includes (all of Pack 1) +
- Timely Reminders
- GSTR-1 Filing (6 months)
- GSTR-3B Filing (6 months)
- Monthly Data Checks
- Basic Sales/Purchase Review
- Filing Confirmation Alerts
- Nil return filing included
- Up to 25 sales + 25 buys/month
- Includes (all of Pack 1) +
- Timely Reminders
- GSTR-1 Filing (12 months)
- GSTR-3B Filing (12 months)
- Monthly Data Checks
- Basic Sales/Purchase Review
- Filing Confirmation Alerts
- Priority Support*
- Nil return filing included
- Up to 25 sales + 25 buys/month
- OR up to 300 invoices/year
Important Note: The pricing listed above applies exclusively to applicants who qualify for Fast Track GST Registration (Rule 14A). For all other GST Registration applications, our standard fee is ₹3500/- plus GST. Please note that additional charges will apply for departmental liaison and drafting necessary replies if the application is found ineligible or necessitates a departmental site visit.
Eligibility Criteria for GST Registration
Registration is mandatory based on aggregate annual turnover, nature of business, and location. The following criteria determine your GST registration requirement as per Section 22 and Section 24 of the CGST Act, 2017.
Service Providers (Normal States)
Mandatory registration if aggregate annual turnover from services exceeds ₹20 Lakhs. Voluntary registration is allowed below this threshold to claim the Input Tax Credit benefit.
Service Providers (Special Category)
For states like Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura, and Sikkim, registration is mandatory when service turnover exceeds ₹10 Lakh annually under the proviso to Section 22(1) of the CGST Act.
Goods Suppliers (Normal States)
Registration is required when aggregate annual turnover from the supply of goods exceeds ₹40 Lakhs. States like J&K and Assam have also opted for this higher turnover threshold limit.
Goods Suppliers (Special Category)
For special category states, goods suppliers must register when their turnover exceeds ₹20 Lakh. Telangana and Puducherry also follow the ₹20 Lakh threshold limits for goods supply.
Rule 14A Fast-Track Opt-In
An optional simplified scheme for all businesses with a monthly B2B output tax liability below ₹2.50 Lakhs. Enables a 3-day auto-approval via electronic grant under Rule 9A of the CGST Act.
Inter-State Suppliers
Registration is compulsory for any inter-state taxable supply of goods or services of more than 20 Lakh, regardless of turnover volume, as per Section 24(i) of the CGST Act, 2017. No exemption applies.
E-Commerce Operators & Sellers
Mandatory for e-commerce operators collecting TCS and all sellers on platforms. Small intra-state sellers below the threshold may be exempt under Section 24(ix) and the recent amendments.
Casual Taxable Persons
Registration is required for individuals who occasionally supply goods or services in a territory where they have no fixed place of business, such as at exhibition stalls or trade fairs.
Note: Does a freelancer providing services to an overseas client need registration?
Legally, a freelancer located in India, exclusively providing services to overseas clients, with an aggregate turnover below ₹20 Lakhs, is not required to register for GST. While Section 24 of the CGST Act typically mandates registration for inter-state supplies (which includes exports), the government issued Notification No. 10/2017-Integrated Tax specifically to exempt service providers with a turnover up to ₹20 Lakhs from this requirement. However, staying unregistered means you cannot file a Letter of Undertaking (LUT), which is the standard procedure to export services without paying tax, nor can you claim refunds on the GST paid for your business inputs (like laptops or internet). Therefore, while you are fully compliant without a GST number under the current law, many freelancers choose voluntary registration to facilitate smoother foreign currency remittances with banks and to claim tax refunds.
GST Registration Pathways & Scheme Comparison
The 2025 GST reforms introduce multiple registration pathways based on your business profile and risk assessment. Rule 9A enables electronic grants within three working days for low-risk applicants, while Rule 14A provides an opt-in simplified scheme for small B2B taxpayers. Choose your registration track and tax scheme carefully based on your business needs.
| No | Feature | Regular Scheme | Composition Scheme | Rule 14A (Fast-Track) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Target Applicants | Businesses with higher B2B volume or large-scale operations | Small retailers with a B2C focus and limited compliance capacity | Small taxpayers with monthly B2B output tax ≤ ₹2.5 Lakh |
| 2 | Turnover/Tax Limit | No Upper Limit | < ₹1.5 Crore (Goods) / ₹50 Lakh (Services) | Monthly B2B Output Tax ≤ ₹2.5 Lakh |
| 3 | Approval Timeline | 7-30 Working Days (Standard Track) | 7-30 Working Days | 3 Working Days* (Fast Track) |
| 4 | High-Risk Scenario | Up to 30 days if biometric verification is required under Rule 8(4A) | Up to 30 days if biometric verification is required | Up to 30 days if flagged for GSK visit |
| 5 | Input Tax Credit | ✅ Available | ❌ Not Available | ✅ Available |
| 6 | Inter-State Supply | ✅ Allowed | ❌ Not Allowed | ✅ Allowed |
| 7 | E-Commerce Sales | ✅ Allowed | ❌ Not Allowed | ✅ Allowed |
| 8 | Applicable Tax Rate | 5% to 28% (Slab-wise) | 1% to 6% (Fixed) | Standard Slab Rates (5%-28%) |
| 9 | Return Filing | Monthly/Quarterly (GSTR-1/3B) | Quarterly (CMP-08) | Monthly (GSTR-1/3B) |
| 10 | How to Opt | Default registration path | Select the Composition option in REG-01 | Select "Yes" for Rule 14A in REG-01 |
| 11 | Key Restriction | None | Cannot supply inter-state or via e-commerce | Cannot hold another Rule 14A in the same State/UT under the same PAN |
*For low-risk applicants identified by the system under Rule 9A
GST Registration
Setindiabiz simplifies online GST registration, providing expert consultation and documentation support for businesses of all sizes, ensuring legal recognition and tax compliance via the official portal (www.gst.gov.in). Choose us for a transparent, hassle-free process that lets you focus on growth.
Documents Required for GST Registration
Submit original, clear, and accurately matched documents to ensure "Low Risk" classification and qualify for 3-day approval under the Simplified Scheme.
Company & Director
- Registration CertificateOfficial document issued by MCA proving the legal existence of the Company or LLP. Contains CIN/LLPIN, date of incorporation, and registered office address. For a registered partnership firm, the firm registration certificate is required.
- MOA & AOA (for companies)MOA & AOA define the company's objectives, rules, and internal governance structure as filed with the Registrar of Companies.
- Partnership/LLP AgreementLegal agreement defining rights, duties, and profit-sharing ratio of partners. Must be stamped and notarised as per applicable state stamp duty laws.
- Business PAN CardPermanent Account Number issued to the business entity by the Income Tax Department. Mandatory for all GST registrations and financial transactions.
- Board Resolution or AuthorisationResolution passed by directors authorising specific person(s) to sign GST application and act as authorised signatory for all GST-related matters.
Director or Partner
- PAN CardPermanent Account Number of all partners/directors/proprietors. Links the individual tax identity and must be active and linked to Aadhaar for verification.
- Aadhaar12-digit unique identification number for identity verification. Required for biometric authentication during the GST registration process as per GSTN norms.
- Address ProofResidential address proof of promoters/partners. Accepted documents: Aadhaar, passport, voter ID, driving license, or recent utility bills (within 2 months).
- Colored PhotographRecent passport-size photo (JPEG format, max 100KB). Must have a plain white background showing a clear face for identification and authentication purposes.
Office or Premises Proof
Owned Premises
- Ownership ProofProperty ownership deed, sale deed, or allotment letter establishing legal ownership of the business premises by the applicant or company.
- Utility Bill as address proofRecent electricity, water, or telephone bill (within 2 months) showing business address. Validates physical existence and location of business premises.
Rented Premises
- Rent Agreement/Lease DeedValid rental/lease contract between owner and tenant. Must be on stamp paper as per state laws and signed by both parties, with clear tenure details.
- NOC from the OwnerNo Objection Certificate from the property owner permitting commercial use of premises for GST registration. Should be signed and include the owner's contact details.
- Utility Bill as Address ProofA Recent utility bill in the owner's name proving the premises address. Submitted along with the rent agreement to verify the actual location of business operations.
Consented Premises (shared offices)
- Co-working agreementA contract between the applicant and the co-working space provider. Details workspace allocation, tenure, and terms of usage for business operations.
- Owner NOC to Co-WorkingProperty owner's consent allowing co-working operators to sublease/share the premises for commercial purposes. Establishes a chain of authorisation.
- Co-Working NOC to the applicantCo-working space provider's consent permitting the applicant to use the shared premises for GST registration and conduct business activities legally.
- Utility bill as address ProofA recent utility bill for the premises in the property owner's or co-working provider's name, validating the physical address of the shared workspace.
Get Your Document Checklist
Avoid delays and rejections. Receive a comprehensive list of all required documents with format specifications, notarization requirements, and expert tips to ensure your application is accepted on the first attempt.
Step-by-Step GST Registration Process
The timeline depends on the "Risk Rating" of your application. We aim for the Rule 14A path for speed. Fast-track timelines are system-driven and subject to risk profiling.
1
Step 1: Application Filing & Scheme Selection
We file Part-A (TRN) and Part-B of Form GST REG-01 on the GST Common Portal. Crucially, we select the "Opt for Rule 14A" checkbox if your monthly B2B output tax liability is below ₹2.5 Lakhs. This positions your application for the fastest 3-day approval track under the Simplified Registration Scheme introduced in November 2025.
2
Step 2: Aadhaar Authentication
The Authorised Signatory receives an authentication link from GSTN. Low-risk Rule 14A applicants complete OTP-based Aadhaar authentication for instant validation. High-risk applicants (PAN/Aadhaar mismatch, risky PIN codes) must visit a GST Suvidha Kendra for biometric verification under Rule 8(4A) within 15 days.
3
Step 3: Verification & Approval
For low-risk applicants identified by the system, Rule 9A grants registration electronically within three working days without officer intervention. This "deemed approval" enables fast-track GSTIN issuance. If biometrics are required or documents are unclear, officer scrutiny applies, and the decision takes 7 to 30 working days.
4
Step 4: GSTIN Issue & Bank Update
Upon approval, you receive Form GST REG-06 containing your 15-digit GSTIN. Critical: Under Rule 10A, update bank account details within 30 days or before the first GSTR-1/IFF filing. Failure to furnish bank details triggers automatic GSTIN suspension, blocking return filing and invoice generation capabilities.
Talk to Our Experts Today
Have questions? Get personalized advice from our licensed professionals. Discuss your requirements, understand the best options for your situation, and get all your doubts cleared — at no cost.
Understanding Your 15-Digit GSTIN
Every GST Identification Number (GSTIN) is a unique 15-character alphanumeric code that contains encoded information about the taxpayer's registration. Understanding this structure helps verify GST numbers and identify business locations.
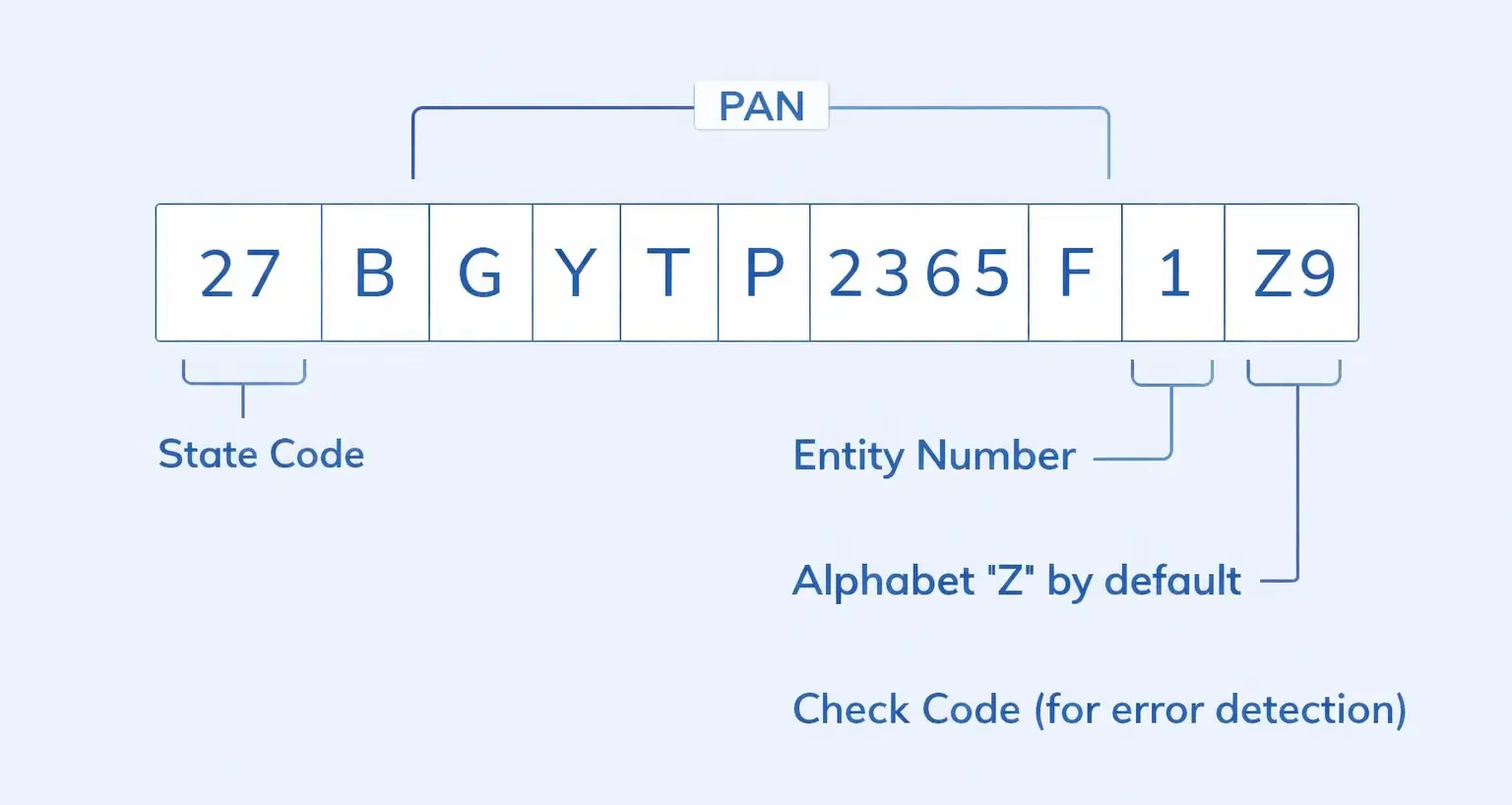
| Position | Characters | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | First 2 digits | State Code – Indicates the state where the business is registered (as per the Indian Census 2011) | 27 = Maharashtra, 07 = Delhi, 29 = Karnataka |
| 3-12 | Next 10 characters | PAN Number – The Permanent Account Number of the business entity or proprietor | AAAAA2222B |
| 13 | 13th character | Entity Number – Indicates the number of registrations under the same PAN in the same state (1-9, then A-Z) | 1 = First registration, 2 = Second registration |
| 14 | 14th character | Default Character – Currently "Z" by default, reserved for future use | Z |
| 15 | 15th character | Check Digit – Alphanumeric checksum for error detection, calculated using a specific algorithm. | M |
Benefits of GST Registration
Registering for GST brings practical benefits to your business. It helps you stay compliant with tax laws and opens doors to opportunities that drive growth.
Stay Legally Compliant
Being GST registered ensures your business follows all required tax rules under the CGST Act. It builds confidence among customers, bankers, and business partners.
Claim Input Tax Credits
GST registration lets you claim credits for tax paid on business purchases. This reduces your overall tax expense and improves cash flow significantly.
Boost Business Credibility
A GST number shows your business is officially recognised and trustworthy. Credibility among suppliers, bankers, and clients leads to better business opportunities.
Simplify Your Invoicing
Issue proper GST invoices with your GSTIN. This keeps financial records clear and enables you to claim input tax credits, ensuring invoicing meets legal standards.
Facilitate Interstate Trade
For businesses operating across multiple states, GST registration simplifies the tax process. It removes cascading taxes and enables seamless interstate operations.
Access Government Benefits
Many government schemes and incentives are available exclusively to GST-registered businesses. MSMEs can access subsidies, loans, and procurement opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions
- All
- Rule 14A & 3-Day Approval
- Registration Thresholds
- Aadhaar & Biometric
- Process & Timeline
- Special Cases
Rule 14A, effective from 1st November 2025 under Notification No. 18/2025-CT, allows small taxpayers with a monthly B2B output tax liability below ₹2.5 Lakh to opt for a simplified registration scheme. For low-risk applicants identified by the system under Rule 9A, the GSTIN is deemed approved electronically within 3 working days without manual officer intervention, provided Aadhaar authentication is successful, and risk parameters are satisfied.
You are eligible if: (1) You apply for registration under Rule 8 of CGST Rules, (2) Your estimated monthly output tax liability on supplies to registered persons (B2B) does not exceed ₹2.5 Lakhs (including CGST, SGST/UTGST, IGST and Cess), (3) You opt for Aadhaar authentication, and (4) You do not already hold a Rule 14A registration in the same State/UT under the same PAN.
If your monthly B2B output tax liability exceeds ₹2.5 Lakhs, you must file an application for withdrawal from the Simplified Scheme using Form GST REG-32. Upon approval via Form GST REG-33, you transition to Normal Taxpayer status from the first day of the succeeding month. The same GSTIN continues; no new registration is required.
To withdraw, you must: (1) File all returns from registration date to withdrawal application date, (2) File minimum 3 months' returns if withdrawing before 1st April 2026 or minimum one tax period if withdrawing on/after 1st April 2026, (3) Have no pending amendment or cancellation applications, and (4) Have no ongoing Section 29 cancellation proceedings initiated against you.
Yes, the Simplified Registration Scheme is available to all entity types, including Private Limited Companies, OPCs, and LLPs, provided they meet the eligibility criteria—specifically, the monthly B2B output tax liability must not exceed ₹2.5 Lakhs, and Aadhaar authentication must be completed by the Directors/Partners and Authorised Signatory.
The limit is based on output tax liability, not turnover. It includes the total GST amount (CGST + SGST/UTGST + IGST + Compensation Cess) on supplies made to registered persons (B2B supplies) in a month. For example, if your monthly B2B sales are ₹15 Lakhs at 18% GST, your tax liability is ₹2.7 Lakhs, which exceeds the limit.
For goods suppliers in normal states, the threshold is ₹40 Lakhs annual aggregate turnover. For service providers, it is ₹20 Lakhs. In special category states (North Eastern states, Uttarakhand), the limits are ₹20 Lakhs for goods and ₹10 Lakhs for services as per Section 22 of the CGST Act, 2017.
Aggregate turnover under Section 2(6) of the CGST Act includes the total value of all taxable supplies, exempt supplies, exports, and inter-state supplies made by persons having the same PAN, computed on an all-India basis. It excludes inward supplies under reverse charge, CGST/SGST/IGST amounts, and GST Compensation Cess.
Yes, GST registration is compulsory for any person making an inter-state taxable supply of goods or services, regardless of turnover, as per Section 24(i) of the CGST Act. The aggregate turnover threshold exemption does not apply to interstate suppliers.
Yes, voluntary registration under Section 25(3) is common for startups wanting to claim Input Tax Credit on initial purchases, work with corporate clients requiring GSTIN, or establish business credibility. Once voluntarily registered, you must comply with all GST provisions for a minimum period before applying for cancellation.
Yes, persons supplying goods/services through e-commerce platforms where the operator is required to collect TCS must register for GST regardless of turnover, as per Section 24(ix). However, recent amendments provide exemptions for small intra-state sellers below threshold limits on certain platforms.
The Composition Scheme under Section 10 is available for goods suppliers with aggregate turnover up to ₹1.5 Crore (₹75 Lakhs for special category states). Service providers and mixed suppliers can opt for the scheme if turnover is below ₹50 Lakhs, paying tax at 6% (3% CGST + 3% SGST).
From 2025, Aadhaar authentication has become, in practice, the default route for most standard GST registration applicants. Biometric-based Aadhaar verification and in-person document checking are mandated for high-risk or identified applicants under Rule 8(4A). Specific categories like non-resident taxable persons, foreign companies, and government departments may be exempt from Aadhaar requirements.
Biometric verification is triggered when: (1) Your application is flagged as "High Risk" by GSTN's data analytics and risk parameters, (2) You choose not to opt for Aadhaar OTP authentication, (3) There are PAN/Aadhaar mismatches, or (4) Your PIN code or business profile falls under identified risk categories.
After submitting Form GST REG-01, you will receive an email notification. If selected for biometric verification, the email will contain a link to book an appointment at the nearest GST Suvidha Kendra (GSK) along with jurisdiction details and the required document list, instead of the standard OTP authentication link.
Carry: (1) Appointment confirmation email (hard/soft copy), (2) Original Aadhaar Card and PAN Card of all Promoters/Partners and Authorised Signatory, (3) Original copies of all documents uploaded with the application, and (4) Jurisdiction details from the intimation email. Verification must be completed within 15 days.
As per the current GSTN advisory practice, promoters and directors may complete biometric authentication at any GST Suvidha Kendra within their home state, even if registering for business in another state. However, the Primary Authorised Signatory typically must visit the jurisdictional GSK for document verification, where facilitated by GSTN and the jurisdictional officer.
If biometric authentication fails or is not completed within 15 days of submitting Part B of Form GST REG-01, the Application Reference Number (ARN) will not be generated, and the registration process will be stalled. You must update Aadhaar details if there are discrepancies and revisit the GSK within the stipulated time.
TRN (Temporary Reference Number) is generated when you start the application (Part-A submission) and is valid for 15 days. ARN (Application Reference Number) is generated only after successfully submitting Part B and completing Aadhaar/Biometric verification. ARN is used for tracking application status.
For low-risk Rule 14A applicants identified by the system under Rule 9A, deemed approval occurs within 3 working days. For standard applications, deemed approval kicks in after 7 working days if the officer takes no action. For biometric verification cases, the officer has up to 30 days to approve, reject, or raise queries.
Under Rule 10A, valid bank account details linked to business PAN must be furnished within 30 days of registration or before filing the first GSTR-1/IFF, whichever is earlier. Failure to comply results in automatic suspension of GSTIN by the system, blocking your ability to file returns and issue invoices.
No, once the ARN is generated, you cannot edit the application. If the officer raises a query through Form GST REG-03, you can file clarifications and corrections through Form GST REG-04 within 7 working days. For post-registration changes, file an amendment application through Form GST REG-14.
Class-3 DSC is mandatory for Companies (Private Limited, Public, OPC) and LLPs. For Proprietorships, Partnership Firms, and HUFs, the application can be e-verified using Aadhaar-based E-Sign (Electronic Signature) without requiring a DSC.
Standard registration typically takes 7-21 working days, depending on risk assessment. Low-risk applications are approved within 7 days. Applications requiring document verification, premises inspection, or those flagged for additional scrutiny may take up to 21-30 working days.
Yes, you can have separate GSTINs for different states (mandatory for inter-state business). Within the same state, you can apply for "Vertical-wise" registration under Section 25(2) if you have distinct business verticals. Each registration must maintain separate compliance and books of accounts.
A Casual Taxable Person occasionally supplies goods/services in a territory where they have no fixed place of business (e.g., exhibition stalls, trade fairs). CTP registration under Section 24(ii) is valid for 90 days, extendable by another 90 days. Estimated tax liability must be paid in advance at the time of registration.
Use the "Search Taxpayer" tool on the GST Portal (www.gst.gov.in). It confirms the Legal Name, Trade Name, Registration Status (Active/Cancelled/Suspended), Constitution, and whether the taxpayer has filed recent returns.
Yes, if you close your business, turnover falls below the threshold, or transfer the business, you can apply for cancellation using Form GST REG-16. All pending returns must be filed, and any outstanding tax liability must be paid before cancellation is approved under Section 29.
Yes, you can apply for "Revocation of Cancellation" using Form GST REG-21 within 30 days of the cancellation order (extendable by another 30 days on application to Additional/Joint Commissioner). All pending returns must be filed with applicable late fees before revocation is processed.
The Proper Officer can cancel your registration suo-moto under Section 29(2) if you: fail to conduct business from the registered premises, issue invoices without actual supply, do not file returns for 6 consecutive months (taxpayers) or 3 consecutive returns (composition dealers), or obtain registration through fraud/misrepresentation. Regular compliance and timely filing prevent suo-moto cancellation.