Guide on the Company Registered Office : The Legal Requirement Under Section 12 of the Companies Act
Overview: This post explains what a registered office is, its purpose and the legal requirements to select and maintain a registered office, and clarifies the difference between a registered office and a corporate office. Every company registered in India needs to have a Registered Office as per Section 12 of the Companies Act 2013. This is the official address where all the government communications are received, and the company has to keep all the statutory records and registers for inspection. A registered office is more than just an address – it’s a compliance pillar.
What Is the Registered Office of a Company?
A company can have multiple locations—corporate offices, main offices, branch offices, corporate headquarters, or regional facilities. Yet among these, the Registered Office stands out as the official address recognised by the Registrar of Companies (ROC) as per section 12 of the Companies Act 2013. All statutory records, registers, and financial accounts are kept at the registered office of the company. All formal correspondence—including letters, notices, and legal communications from the ROC, government bodies, banks, investors, and the general public—is directed here.
In other words, your company’s Registered Office is effectively its primary, legally recognised business address, even if other offices exist. From displaying the company’s name board to filing the updates with ROC (via Form INC-22) – complying with the legal requirements ensures smooth functioning and avoids a penalty of ₹1,000/day for non-compliance. It is also important to notify relevant regulatory bodies, such as the Securities and Exchange Board, especially for listed companies, to ensure regulatory compliance.
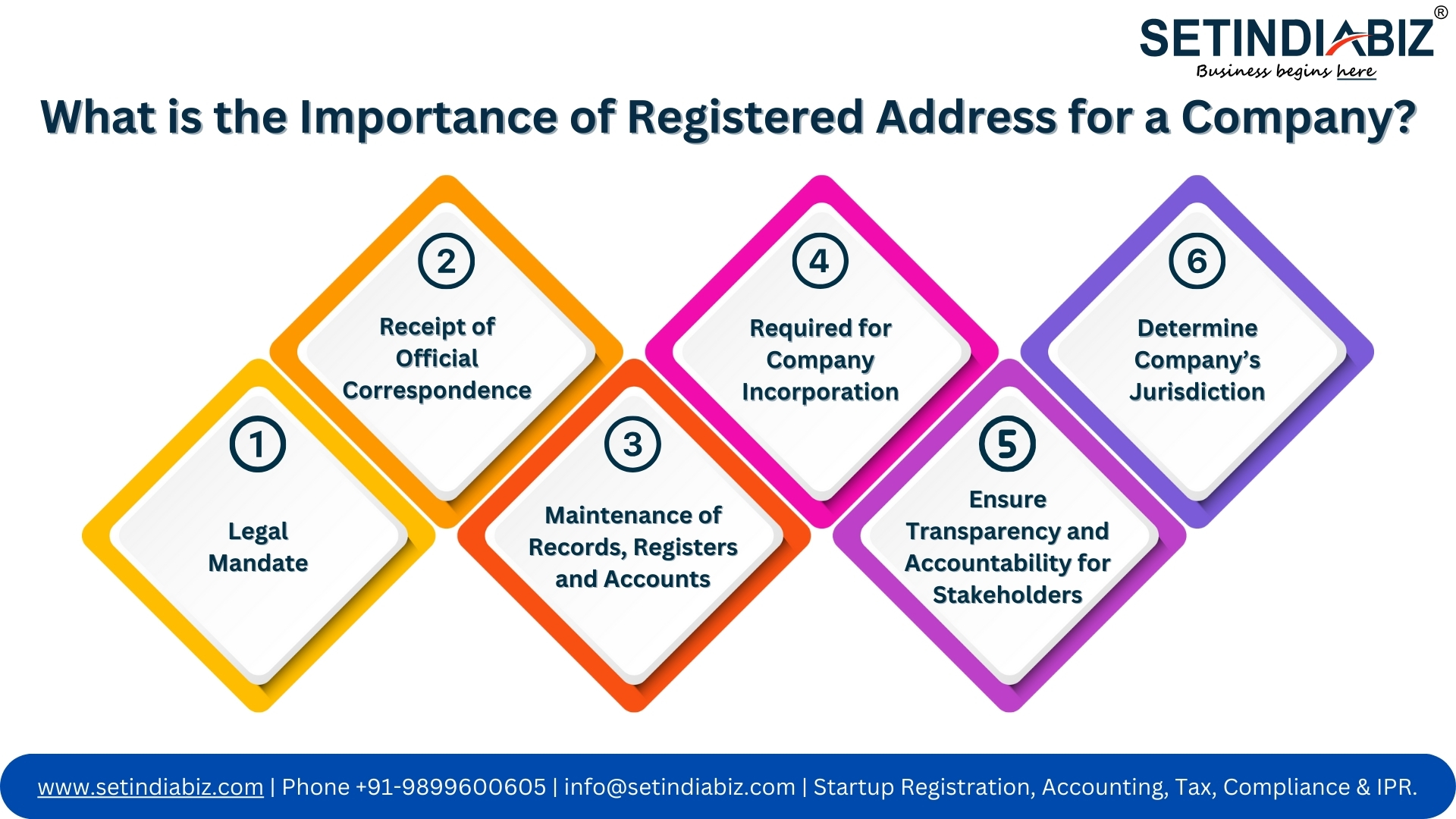
Importance of the Registered Address for a Company
The significance of a company’s registered address can hardly be overstated. It serves multiple crucial functions—from ensuring legal compliance and maintaining critical records to demonstrating accountability and transparency for all stakeholders, including shareholders, creditors, government authorities, key management personnel, employees, and clients. Below are several in-depth reasons illustrating why a company’s registered office address is so vital.
- Legal Mandate: Under Section 12 of the Companies Act 2013, every company incorporated in India must have a registered office. This address is used for all official communication, notices, and documents from stakeholders such as the Registrar of Companies (ROC), tax authorities, investors, and creditors. The registered office must fulfil all the requirements mentioned in Section 12 of the Companies Act 2013.
- Receipt of Official Correspondence: Since the registered office address is on public record and verifiable on the Ministry of Corporate Affairs website at www.mca.gov.in, it is the default location for receiving all official communications. Government agencies, regulatory bodies, creditors, shareholders, directors, and customers send important documents such as notices, legal summons, legal documents, and all other official intimations to the registered office of the company, which is updated in the records of the MCA.
- Official Display of Address and Name: As per section 12 of the Companies Act, the name board or company signboard must be affixed/displayed predominantly on the premises where the registered office of the company is situated. Under their respective Shops & Establishment Acts, some states also require the name board to appear in the regional language alongside English. The name plate must contain the following details:
- Complete company name
- Registered office address
- Corporate Identification Number (CIN)
- Contact details (phone number, email, and, if applicable, website)
- Maintenance of Records, Registers and Accounts: A Company must maintain all its official records, important documents like Account Books, MOA, AOA, and essential statutory registers at its Registered Office of Company. The records of the company must be kept available for inspection by the government authorities and other stakeholders during office hours. This is not only a mandatory requirement under law but also a practical advantage, as it is here that its principal business operations are conducted. Companies may maintain their books of account at a different location by notifying the ROC within seven days of the decision.
- Books of Account at Other Address: The company can maintain the books of accounts elsewhere within the same city with the approval of the board of directors of the company. The company must file an intimation to the ROC within seven days of the board’s approval about the address where the books of account shall be maintained. The intimation of the other office where the books of account shall be maintained is filed in the prescribed form AOC-5, and after the approval of the same, the Master data of the company at www.mca.gov.in also displays the additional office address where the company maintains the books of account.
Legal Requirements for a Registered Office
A registered office is a crucial aspect of a company’s legal identity in India. The Companies Act, 2013, specifies legal obligations related to a company’s registered office. The registered office must be a physical location in India, and the company must record the registered office address in its incorporation documents. The company must also make the registered office address available on public record. The Ministry of Corporate Affairs plays a crucial role in the registration and regulation of companies in India.
It is important to notify relevant regulatory bodies, such as the Securities and Exchange Board, especially for listed companies, to ensure regulatory compliance.
The registered office address is used for multiple purposes, especially while filing important applications to government authorities for tax and regulatory compliance. Thus, it is necessary to have documented evidence for your registered office, establishing both the company address and existence at the concerned location. You can use the following for this purpose:
- Utility bills (electricity, water, gas, etc.)
- Rent agreement or lease deed
- No objection certificate (NOC) from the landlord
- Proof of ownership or tenancy
The company must notify the Registrar of Companies of any changes to the registered office address. The process involves several key steps, including board meetings, shareholder approvals, and filings with the ROC. This ensures that the registered office address is always up-to-date and compliant with the legal requirements set forth by the Companies Act, 2013.
Registered Office Address for Company Incorporation
At the time of incorporation of a company, the promoters have to submit proof of the registered office address along with an NOC from the owner of the premises. Though the company can be incorporated into a communication address, in that case, the registered office address also needs to be filed with the ROC within 30 days of its incorporation. Here are the key points to consider:
- Premises Type: You can have a registered office on residential or commercial land; check if the office location complies with all local laws and does not violate state-specific commercial or residential use laws. The office should be in a fully built building, not under construction or renovation. It is essential to have a physical office space to meet legal requirements and ensure the necessary privacy and security.
- A lockable space: The registered office must be a lockable space to follow the requirements of section 12 of the Companies Act, 2013, as necessary official records and statutory documents must be safely kept.
- No Objection Certificate (NOC): If you rent the premises, get a No Objection Certificate from the property owner. This document will confirm that the owner is okay with using their property as your registered office. If the property is self-owned, keep ownership documents handy for verification.
Can a Coworking/Shared/Virtual Office Serve as a Registered Office?
Under section 12 of the Companies Act 2013, the registered office of the company must be a physical, lockable space where statutory records are stored and accessible for inspection. Registered offices must fulfil specific requirements, such as being a physical and lockable space, for the proper storage of official company records and for receiving legal correspondence. Here’s how different office types comply:
- Coworking/Shared Office: Legally, you can incorporate the company at the registered office in a coworking or shared office, but with the strict condition that the company must have exclusive access to a lockable area within the shared space for storing statutory records. You also have to ensure that the company nameplate or display board can be displayed on the registered office and that the owner of the premises will provide the electricity bill and NOC. Shared desks or non-lockable areas do not qualify, and the risk of ROC rejection is very high.
- Virtual office: It is not allowed unless it includes a physical, lockable space. A mailing address-only virtual office (e.g., PO Box) is invalid as a registered office.
Conclusion
We have explained the meaning and significance of the registered office for the company in a very simple and lucid manner for the benefit of startups. Setindiabiz provides several compliance services, including incorporation and further secretarial compliance. You are encouraged to send your feedback and suggestions to improve this blog.