Flow Chart of Trademark Registration
Overview : Are you facing trouble understanding the different stages of Trademark Registration? No Worries, you are not alone. This Trademark Registration Process Flow Chart is specially designed for you! This blog provides you with a comprehensive step-by-step guide of the process to help you navigate through swiftly and efficiently.
Since Trademark Registration is a legally complex process, a flow chart for Trademark Registration can be the best and the simplest way to understand it. So, the purpose of this blog is to guide you through the trademark registration process flowchart, providing valuable insights for easy stepwise navigation.
All of these issues can be avoided if everyone has a good understanding of trademarks. So, let’s get right into it today and discuss trademarks, trademark searches India, and the plethora of characteristics.
From initial research to application preparation, examination, publication, and registration, this blog will equip you with the knowledge to confidently safeguard your brand assets. So, embark with us on this enlightening journey as we unravel the intricacies of trademark registration in India.
What is the process of Trademark Registration?
Trademark registration is a crucial legal process designed to protect unique brand assets and provide exclusive ownership rights to their owners. It involves obtaining legal recognition and safeguards against plagiarism for trademarks such as logos, names, symbols, or phrases, used in connection to specific goods or services. In India, trademark registration is governed by the Trade Marks Act, 1999, and administered by the Office of the Controller General of Patents, Designs and Trademarks.
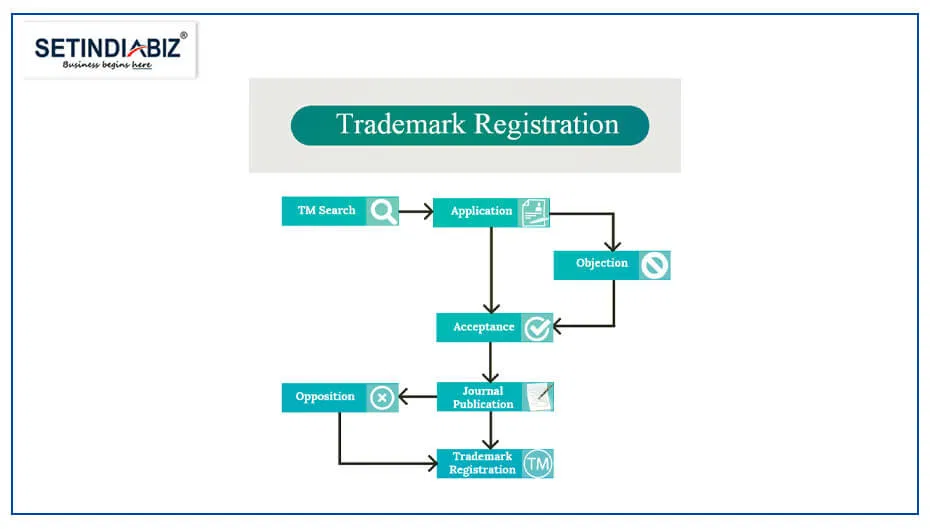
The process of trademark registration in India involves several stages. Here is a brief overview of the typical process:
- Trademark Search: Conduct a thorough search to ensure that your proposed trademark is unique and not already registered or being used by others in a similar or related class of goods/services. This will help you assess potential conflicts and objections during the Trademark Registration process.
- For this, you need to determine the appropriate class or classes of goods or services for registering your Trademark, based on the Nice Classification system. The Nice Classification system categorizes goods and services into 45 classes, with each class representing a distinct category.
- Application Filing: Prepare and file the trademark application with the Office of the Controller General of Patents, Designs and Trademarks (CGPDTM) in India. The application should include the necessary details, such as the Applicant’s Name, Address, Trademark Representation, and a list of Goods or Services for which the mark will be used.
- Objection / Acceptance by the Trademark Examiner: Once the application is filed, the trademark office examines it to assess compliance with legal requirements. They review factors such as distinctiveness, similarity to existing trademarks, and adherence to trademark laws. If any objections or discrepancies are found, the applicant may need to address them and provide suitable responses within 30 days of receiving the objection. If the replies are satisfactory, the examiner will proceed to the next stage.
- Journal Publication: If the trademark application passes the examination stage, it is published in the Trademarks Journal. This publication allows third parties to oppose the registration within a specified period of four months. If no opposition is raised, the application proceeds further to the last stage.
- Opposition: However, if a third party raises opposition during the time the mark is published in the Trademark Journal, the applicant will have to file an appropriate reply and counterevidence to the opposing party. If the opposing party does not find the reply satisfactory, then the Department shall call a show cause hearing to resolve the issue.
- Trademark Registration: Upon successful completion of the publication stage, the trademark registration is granted, and a Certificate of Registration is issued. The registration is valid for ten years from the date of application and can be renewed indefinitely by paying the trademark renewal fees at regular intervals.
It’s important to note that the actual timeline and requirements may vary based on the specifics of the application and any potential objections or oppositions encountered during the process. Working with a qualified trademark attorney or professional can help ensure a smooth and successful registration process. Remember, this overview provides a general outline of the trademark registration process in India. For a more detailed and accurate understanding, seek professional guidance.
Beware of Trademark Infringement
Every firm must have a unique trademark because if any business trademark already exists, the other party has the authority to take strict action against the person who has copied the brand. Trademark registration will protect you from these problems.
The Trademarks Act of 1999 outlines the law for trademark registration, protection, and infringement penalties. Many international and national organizations are working to safeguard intellectual property like trademarks.
In India, trademark protection is handled by the Indian Patent Office, which is governed by the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trademarks. Trademark infringement is defined as the illegal use of a mark that is identical or deceptively similar to a registered mark.
To prevent this, we will go to the following section of the article: trademark search. What exactly is it? Why is it important? What is the difference between symbols "R" and "TM" in Trademark? Let us proceed to clarify a few things.
Why is Trademark Registration Required in India?
Trademark registration offers several key benefits and is essential for various reasons:
Therefore, it implies that if someone tries to register their version of your trademark or any brand identification, they will first pay a penalty fee before proceeding with registration procedures.

Legal Protection: Registering a trademark in India provides legal protection against their unauthorized use, thereby preventing others from imitating or infringing upon them without the permission of the owner. It gives the owner the exclusive right to use the trademark in connection with the goods or services for which it is registered.
Brand Identity and Recognition: Trademarks help establish a unique brand identity and make your goods or services easily recognizable to consumers. Registering your trademark in India ensures that you can build a distinctive brand presence and protect it from being exploited by competitors.
Market Advantage and Business Growth: Trademark registration provides a competitive edge to your business in the market by differentiating your products or services from others. It helps build trust and loyalty among consumers, leading to increased sales, customer retention, and business growth.
Legal Recourse and Enforcement: With a registered trademark, you have stronger legal grounds to enforce your rights and take legal action against infringers in India. It allows you to seek remedies, such as damages and injunctions, to protect your brand’s reputation and market share.
Licensing and Expansion Opportunities: Trademark registration opens doors to licensing and franchising opportunities. It allows you to grant licenses to third parties to use your trademark, generating additional revenue streams and expanding your business presence in India.
Conclusion
Trademark registration in India is a vital process that provides brand owners with exclusive rights and legal protection for their unique brand assets. By understanding and undergoing the above-mentioned process of Trademark Registration in India, the brand owners can get their trademark registered successfully and thus safeguarding their valuable business assets. With a registered trademark, brand owners can confidently navigate the Indian marketplace, enforce their rights, and pave the way for long-term growth and success.
FAQ's
Trademark registration is not mandatory, but it offers legal benefits and protections.
Essential conditions for trademark registration include distinctiveness, non-conflict with existing marks, use in commerce, and adherence to public policy.
™ indicates a claim to a mark, while “®” signifies a registered trademark. You can use ™ as soon as you file a Trademark Application and “®” after your Trademark is registered
Trademarks that are generic, descriptive, confusing, offensive, or functional cannot be registered.
Individuals, businesses, and organizations can apply for trademark registration through the appropriate trademark office. Consulting with a professional is recommended.
Author Bio

Editorial Team | in
Setindiabiz Editorial Team is a multidisciplinary collective of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Advocates offering authoritative insights on India’s regulatory and business landscape. With decades of experience in compliance, taxation, and advisory, they empower entrepreneurs and enterprises to make informed decisions.
