Overview : In this cutthroat competitive environment, companies strive to strengthen their financial positions, thus, often ready to explore innovative strategies to do so. The ‘Conversion of Loans into Equity’ has emerged as an effective strategy. This strategy has a number of benefits, including improved balance sheets and reduced debt. Delve into essential aspects of loan conversion to equity with this detailed and easy-to-understand guide!
In today’s dynamic business environment, companies often look for innovative strategies to sustain and strengthen their financial structure. One such effective strategy is the conversion of loans into equity. This approach can offer multiple benefits including improved balance sheets, reduction in debt, and enhanced investor confidence.
But how exactly does the process of Conversion of Loan into Equity work? What are the regulations outlined in the Companies Act, 2023 governing this transformation? Understanding these complexities can help business owners, investors, and financial professionals make informed decisions.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the conversion of loans to equity, guided by the provisions set under the Companies Act. We’ll discuss the pre-conversion considerations, walk you through the step-by-step conversion process, and delve into the implications post-conversion. This article aims to offer valuable insights and clarity on the subject. So, let’s delve into the world of loan conversions, demystifying the complexities along the way.
Part I: Understanding the Legal Framework
- Definition and Explanation of Relevant Terms: Before delving into the legal framework, it’s crucial to understand the key terms involved. A loan refers to funds borrowed by a company from an individual, institution, or another entity, typically with an obligation to repay the borrowed amount with interest. Equity, on the other hand, represents ownership in a company, often in the form of shares or stock. Conversion refers to the process of converting a loan into equity, where the creditor becomes a shareholder in the company.
- Brief Introduction to the Companies Act and Section 62(3): The Companies Act, 2013 serves as the primary legislation governing the functioning and operations of companies. Section 62(3) of the Companies Act allows for the conversion of loans into equity. This section states that a company may, with the approval of a special resolution passed by its shareholders, convert any of its loans into shares of the company.
- Rules made under the Companies Act: The Companies (Share Capital and Debentures) Rules, 2014 (the “Rules”) play a significant role in providing further provisions and guidance regarding the conversion of loans into equity. These rules establish specific conditions that must be met for a loan to be converted into equity:
Part II: Pre-Conversion Considerations
In order for a loan to be converted into equity, the company must have passed a special resolution at the time of accepting the loan, which specifies that the loan may be converted into equity in the future. This is necessary to ensure that the lender is aware of the possibility of the loan being converted into equity, and that they have agreed to this possibility. The special resolution should specify the following:
- The terms and conditions on which the loan may be converted into equity, such as the date on which the conversion will take place, the number of shares that will be issued in exchange for the loan, and the price per share.
- The procedure for converting the loan into equity, such as the steps that the company and the lender must take in order to complete the conversion.
- The special resolution must be passed by a majority of the company’s shareholders at a general meeting. Once the special resolution has been passed, the company may convert the loan into equity at any time in the future, subject to the terms and conditions specified in the resolution.
Part III: Checklist for Converting a Loan into Equity
- Check if the loan agreement allows for conversion into equity. The loan agreement should specify whether the loan can be converted into equity and the terms and conditions of the conversion.
- Check if the company has passed a special resolution at the time of accepting the loan, which specifies that the loan may be converted into equity in the future. This is necessary to ensure that the lender is aware of the possibility of the loan being converted into equity, and that they have agreed to this possibility. The special resolution must be passed by a majority of the company’s shareholders at a general meeting. Once the special resolution has been passed, the company may convert the loan into equity at any time in the future, subject to the terms and conditions specified in the resolution.
- Check if the company has sufficient distributable profits to cover the amount of the loan that is being converted into equity. This is a requirement under the Companies Act. Important point with respect to the requirement of distributable profit is as under
- Distributable profits are the profits of a company that are legally available for distribution as dividends. In order to convert a loan into equity, the company must have sufficient distributable profits to cover the amount of the loan that is being converted into equity. This is a requirement under Section 62(3) of the Companies Act.
- For example, let’s say a company has a loan of INR 100,000. In order to convert this loan into equity, the company must have distributable profits of at least INR 100,000. If the company does not have sufficient distributable profits, it cannot convert the loan into equity.
- The company can calculate its distributable profits by taking its net profit for the year and subtracting any amounts that are not distributable, such as dividends paid, losses carried forward, and provisions for taxation.
- Once the company has calculated its distributable profits, it can then compare this amount to the amount of the loan that is being converted into equity. If the distributable profits are at least equal to the amount of the loan, then the company can proceed with the conversion.
- Check if the company has the necessary approvals from the shareholders and the lender to convert the loan into equity. The company must pass a special resolution at a general meeting of its shareholders, and the lender must agree to the conversion.
- Check if the company has the necessary documentation in place to complete the conversion. This includes the loan agreement, the special resolution, and the valuation report(if required). Whether a valuation report is required for the conversion of a loan into equity depends on the circumstances.
- If the loan was issued with the option to convert into equity at a predetermined price, then no valuation report is required. This is because the price of the shares to be issued in exchange for the loan is already known.
- However, if the loan was issued without the option to convert into equity, or if the terms of the conversion are not yet agreed upon, then a valuation report may be required. This is to ensure that the shares issued in exchange for the loan are fairly valued.
- The Companies (Share Capital and Debentures) Rules, 2014, require a valuation report if the conversion of the loan into equity results in the issue of shares for a consideration other than cash. This means that if the shares are issued for a consideration other than cash, such as for the transfer of assets or for the provision of services, then a valuation report is required.
- The valuation report should be prepared by a valuer registered with the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI). and should be based on the market value of the shares at the time of the conversion. The valuation report should also consider the terms of the conversion, such as the price per share and the number of shares to be issued.
Part IV: Step by Step Process for Conversion of Loan to Equity
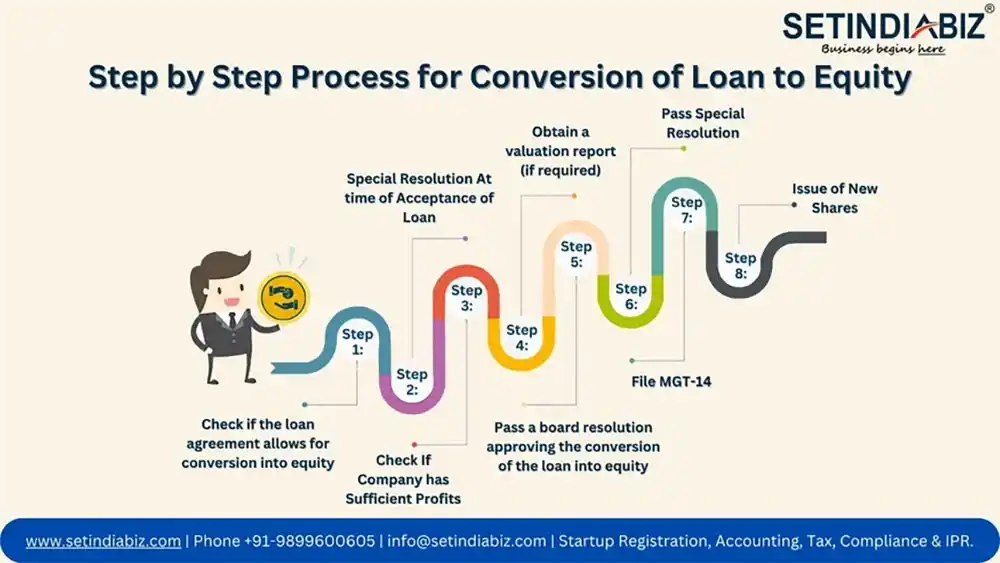
Step 1: Check if the loan agreement allows for conversion into equity: The loan agreement should specify whether the loan can be converted into equity and the terms and conditions of the conversion. If the loan agreement does not allow for conversion into equity, then the company cannot convert the loan into equity.
Step 2: Special Resolution At time of Acceptance of Loan: Check if the company has passed a special resolution at the time of accepting the loan, which specifies that the loan may be converted into equity in the future. This is necessary to ensure that the lender is aware of the possibility of the loan being converted into equity, and that they have agreed to this possibility.
Step 3: Check if the company has sufficient distributable profits to cover the amount of the loan that is being converted into equity.
Step 4: Obtain a valuation report (if required): The Companies (Share Capital and Debentures) Rules, 2014, require a valuation report if the conversion of the loan into equity results in the issue of shares for a consideration other than cash. This means that if the shares are issued for a consideration other than cash, such as for the transfer of assets or for the provision of services, then a valuation report is required.
The valuation report should be prepared by a registered valuer and should be based on the market value of the shares at the time of the conversion. The valuation report should also consider the terms of the conversion, such as the price per share and the number of shares to be issued.
Step 5: Pass a board resolution approving the conversion of the loan into equity: The board of directors of the company must pass a resolution approving the conversion of the loan into equity. The resolution should specify the following:
- The terms and conditions on which the loan is being converted into equity.
- The number of shares that are being issued in exchange for the loan.
- The price per share.
Step 6: Pass Special Resolution: Call a general meeting of the shareholders and pass a special resolution approving the conversion of the loan into equity. The shareholders of the company must pass a special resolution approving the conversion of the loan into equity. The special resolution must be passed by a majority of the shareholders present and voting at the general meeting.
Step-7: File MGT-14. The special resolution passed in the shareholders meeting must be filed with the ROC in the prescribed form MGT-14 is a form that must be filed with the Registrar of Companies within 30 days of the date of the general meeting approving the conversion of the loan into equity.
Step 8: Issue of New Shares: The company must issue new shares to the lender in exchange for the amount of the loan that is being converted into equity. The shares should be issued at the price per share that was specified in the board resolution and the special resolution. PAS-3 Form needs to be filed to the ROC for issue of new shares.
Part V: Post-Conversion Implications
Following the conversion of loans into equity, there are several implications, both financial and operational, that a company must understand:
- Balance Sheet Improvement: Once the loan is converted into equity, the liability section of the balance sheet decreases, which in turn decreases the company’s financial risk and improves the debt-to-equity ratio.
- Potential Dilution of Existing Shareholders: The conversion of loans into equity typically results in the issuance of new shares, which can dilute the shareholding percentage of existing shareholders. This could impact the distribution of dividends and voting rights.
- Increased Compliance: With a new class of shareholders, there may be an increase in reporting and disclosure obligations to comply with corporate governance norms.
- Tax Implications: Conversion of loans into equity can have several tax implications. For instance, the conversion may trigger a taxable event depending on the jurisdiction. It’s recommended to consult with a tax professional to understand these implications.
- Changes in Control and Decision Making: If the lender, who has now become a shareholder, holds a significant percentage of shares, it may influence the decision-making process and the overall direction of the company.
- Enhanced Investor Confidence: A healthier balance sheet and reduced financial risk can boost investor confidence and may make the company more appealing to future investors.
Conclusion
The loan conversion into equity can be beneficial for the betterment of a company’s financial health and also appeal to investors. The conversion process primarily consists of navigating a regulatory framework and understanding the financial and operational implications. As a result, it’s advisable to the companies looking to opt for this strategy, to seek legal and financial guidance from the experts to finalize the process of conversion of loan into equity properly.
FAQ’s
Can any type of loan be converted into equity under the Companies Act?
What happens if our company doesn’t have enough distributable profits for conversion?
- Wait until profits meet the loan amount, or
- Explore alternative debt restructuring options
