Overview : For startups and small businesses, monthly financial statements and reports are the backbone of an informed decision-making process. They provide a snapshot of the business’s financial performance, guiding founders and managers in strategy, compliance, and planning. By reviewing the financial reports every month, businesses can ensure compliance with laws, adjust their budgets, and make timely decisions to foster growth. In short, monthly MIS and financial statements serve as an early warning system and roadmap for a company’s financial journey.
Understanding Key Reports
The financial reporting for companies or LLPs consists of several key reports that together form the Monthly MIS package. The most important ones include the Trial Balance, Profit & Loss Account, and Balance Sheet, as well as the detailed statement of accounts (ledger) for important customers of vendors, each serving a unique purpose in verifying accuracy and assessing performance. These core reports ensure that your books are error-free and provide insights into profitability and financial health. Below, we break down each report and explain why it matters:
Trial Balance
A trial balance is a foundational bookkeeping report that lists all ledger account balances (both debits and credits) at a given time. Its primary purpose is to check that total debits equal total credits, ensuring the accuracy of the double-entry accounting system. Startups and small businesses typically prepare a trial balance at the end of every month or reporting period.

A Trial Balance is the starting point for creating accurate financial statements. It compiles the ending balances of all general ledger accounts—classified as debit or credit—to ensure that the total of all debits equals the total of all credits. This essential check maintains the integrity of the double-entry accounting system.
- Debit Balances: Generally represent assets (like cash, inventory, or receivables) and expenses (such as rent, utilities, or salaries). A debit balance indicates that the sum of debit entries in that account exceeds the sum of credit entries.
- Credit Balances: Typically linked to liabilities (e.g., loans, creditors/payables), income (such as revenue from sales), and equity (like share capital or retained earnings). A credit balance means the sum of credit entries is higher than the sum of debit entries.
When the debit and credit columns in your Trial Balance match, it suggests that your books are arithmetically correct, though it doesn’t guarantee the absence of every possible error. Nonetheless, it is a crucial control mechanism to spot posting mistakes.
Profit & Loss Account
The Profit & Loss Account (P&L) – also known as the income statement – shows your income, expenses, and profit or loss over a period (usually a month, quarter, or year). It summarizes the revenues earned and expenses incurred by the business, ultimately revealing whether you made a profit or suffered a loss during that time. For startups and SMEs, the P&L is crucial because it measures operating performance and sustainability.
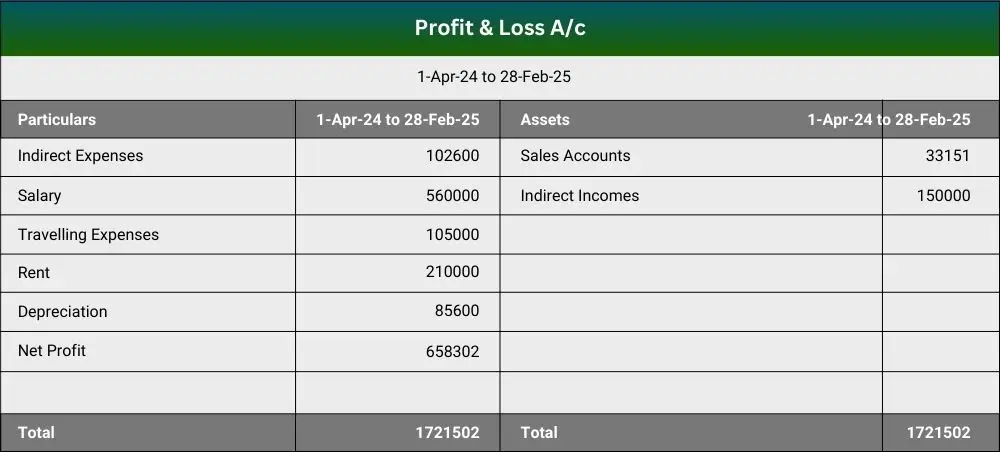
The Profit & Loss Account shows income, expenses, and net profit or loss over a specific period (monthly, quarterly, or annually). For startups and SMEs:
- Revenue (Sales/Income): The total earnings from goods sold or services rendered. The revenue section will also include revenue-generating items that indirectly add revenue, such as interest on fixed deposits or income arising out of the investments.
- Expenses (Direct & Indirect): Costs associated with producing goods/services (Cost of Goods Sold) and operational expenses (rent, salaries, marketing, etc.). The indirect expenses would contain non-cash expenses such as depreciation.
- Net Profit or Loss: The surplus (or deficit) remaining after all expenses are deducted from revenue.
By reviewing this statement monthly, you can quickly identify profit trends, detect cost overruns, and measure whether your business model is currently viable or needs adjustment.
Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet provides a snapshot of the financial position of a business at a specific point (e.g., month-end or year-end). It lists what the business owns, what it owes, and the net worth belonging to owners/shareholders. In other words, it is a statement of assets, liabilities, and equity. Assets include things like cash, bank balances, receivables, inventory, equipment – all the resources that provide future benefit. Liabilities cover obligations such as loans, payables, or any debt owed by the company. Equity represents the owners’ stake (initial capital plus retained earnings or losses).
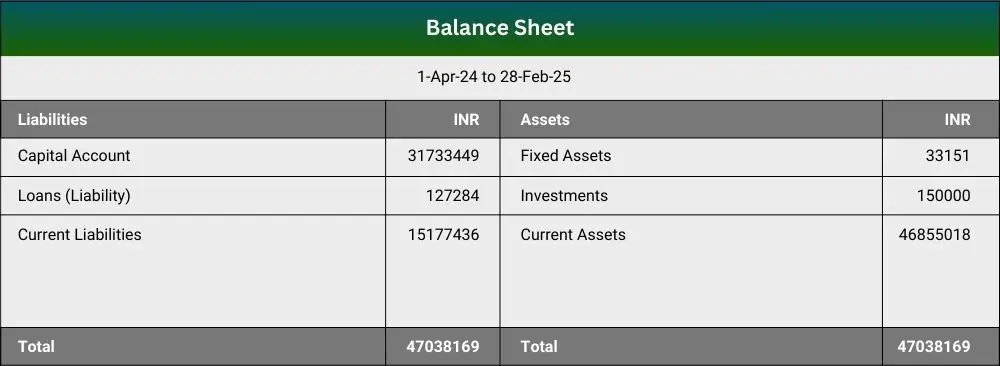
The balance sheet follows the equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity
This statement helps gauge solvency, liquidity, and leverage. A balanced, well-structured Balance Sheet is a sign of a healthy business, demonstrating the ability to meet short-term obligations while also indicating long-term sustainability. Stakeholders often scrutinize the balance sheet: creditors check it to assess solvency and creditworthiness, while investors look at the equity and asset quality to gauge the company’s value. In sum, the balance sheet reveals the financial health of your SME – showing liquidity (can you meet short-term obligations?), leverage (how much debt vs. equity?), and the overall net worth of the business.
Reporting in Schedule III for the companies:
While monthly MIS reports are often concise and management-focused, Schedule III statements provide a more comprehensive view meant for statutory compliance, investor scrutiny, and regulatory review. Thus, it’s important to reconcile and adjust your monthly figures to the official format when preparing audited financial statements to ensure compliance with the Companies Act.
Legal Framework for Financial Reporting
Financial reporting isn’t just good practice – it’s also a legal requirement. Various laws govern how businesses maintain books and report financial information. Non-compliance can lead to penalties, so it’s important for startups and SMEs to be aware of these provisions. Here’s a brief overview of the legal framework in India that impacts accounting and MIS reporting:
- Companies Act, 2013: Sections 128 & 129 provides that the Companies must maintain proper books of account (on an accrual basis and using the double-entry system) and prepare true and fair financial statements (Balance Sheet, Profit & Loss, etc.). The account of the company must also be maintained in an accounting system that records logs.
- LLP Act, 2008: Similarly, Limited Liability Partnerships are obligated to maintain proper financial records. Section 34 of the LLP Act stipulates that an LLP must keep books of accounts such that they show a true and fair view of the state of affairs of the LLP (Professional Virtual CFO Services | Focus on Business Growth). LLPs have to prepare a Statement of Account and Solvency and file it annually with the Registrar.
- Income Tax Act, 1961: The tax law requires businesses and professionals above certain income/turnover limits to maintain books of accounts (Section 44AA) and get accounts audited (Section 44AB) if thresholds are exceeded. Even if you’re below the limit, keeping organized accounts is necessary to correctly calculate taxable income. Non-maintenance of required books can attract penalties – as per Section 271A, failure to keep books as mandated can result in a Rs. 25,000 penalty
- GST Act, 2017: Goods and Services Tax laws require every registered person to maintain detailed accounts and records of sales, purchases, stock, and tax paid/collected. Section 35 of the CGST Act and Rule 56 lay down the record-keeping requirements for GST-registered businesses. Proper maintenance of invoices and account books is critical, as monthly or quarterly GST returns must match your books. Any mismatch can lead to notices or audits. By doing monthly MIS that reconciles your sales and expenses with GST liabilities, you ensure that GST returns (GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, etc.) are filed accurately.
By understanding these legal requirements, startups and SMEs can appreciate why regular financial reporting is not optional. Keeping books up-to-date through monthly MIS reporting puts you in a strong position to meet all these compliance obligations with ease.
Why Outsource Accounting & MIS Reporting?
Handling accounting and MIS reporting in-house can be challenging for startups and small businesses. Many are discovering that outsourcing these functions to experts yields better results at lower cost. In fact, you’re in good company if you consider outsourcing – over 85% of businesses in India outsource their tax and accounting work to consultants, and for small businesses the figure is even higher (Professional Virtual CFO Services | Focus on Business Growth). Here are some compelling reasons to outsource your bookkeeping and MIS reporting:
- Cost and Time Efficiency: Outsourcing spares you from hiring a full in-house accounting team. You pay only for the services you need. Entrepreneurs can focus on core business activities rather than bookkeeping chores.
- Expertise and Accuracy: Professional accountants and Virtual CFO services stay updated on legislative changes and ensure error-free, compliant books. Avoid costly mistakes that can lead to penalties or tarnish your brand in front of investors and regulators.
- Scalability: As your startup grows, an outsourced partner can quickly scale services to meet increasing transaction volumes or new compliance requirements. You can add specialized support (like CFO-level insight) without hiring full-time staff.
- Value-Added Insights: Many outsourced providers offer custom MIS dashboards, ratio analysis, and strategic forecasting. Monthly reviews come with expert commentary to help you interpret financial trends and plan effectively.
Leverage Setindiabiz’s Virtual CFO Services
Setindiabiz’s Virtual CFO services cater specifically to startups and SMEs, streamlining accounting, compliance, and strategic financial management. Our team ensures monthly statements are accurate, comply with all Indian laws, and offer guidance on optimizing your financial operations.
Conclusion
In summary, the key takeaways are: prioritize regular financial reporting, use the insights to steer your business, and don’t hesitate to seek expert assistance to streamline the process. A well-implemented monthly MIS can be the difference between a business that merely survives and one that thrives. So, invest the time to get your financial reporting right – and if you need, engage professionals to help – and empower your startup/SME to achieve greater compliance, efficiency, and growth. Your future self (and your investors, auditors, and regulators) will thank you for it!
FAQ’s
What does Setindiabiz’s Virtual CFO service include?
What financial reports and compliance filings will I receive every month?
- Trial Balance,
- Profit & Loss Account
- Balance Sheet, and
- Multi-ledger Pdf Printout
Will the Virtual CFO handle bookkeeping and ledger management?
How does Setindiabiz ensure my GST filings are accurate and timely?
How is TDS calculated, deducted, and filed on my behalf?
- Accurate deduction as per Income Tax Act provisions
- Timely deposit of TDS with the government
- Filing of quarterly TDS returns (Form 24Q, 26Q, etc.)
- Providing TDS certificates (Form 16/16A) to employees and vendors
How does the Virtual CFO assist in advance tax calculations and payments?
- Computes advance tax liability every quarter
- Prepares a tax payment schedule to avoid interest penalties
- Guides clients on making online payments via government portals
What MIS reports will be provided, and how will they help in decision-making?
- Revenue & Expense Analysis
- Cash Flow Statements
- Profitability Trends and Variance Analysis
- Debtor & Creditor Reports
- Tax Compliance Status Reports
Will the CFO provide insights into my company’s financial health?
Can I request customized financial reports for my industry or investor needs?
- Investor Financial Projections
- Business Valuation Models
- Departmental Profitability Reports
Will the CFO help optimize taxes and reduce liabilities?
How does Setindiabiz ensure compliance with Indian laws?
- Companies Act, 2013 (proper bookkeeping, annual returns, statutory audit support)
- Income Tax Act, 1961 (TDS, advance tax, corporate tax filings)
- GST Act, 2017 (monthly/quarterly GST return filing and reconciliations)
- Labour Laws (if applicable): We ensure that clients meet all legal deadlines and avoid penalties.
Will the CFO assist with cash flow forecasting and budget planning?
- Expected cash inflows and outflows
- Fixed and variable costs
- Seasonal financial trends
- Working capital requirements
Can the CFO help in financial projections and investor presentations?
- Business financial forecasting (3-5 years)
- Investment pitch deck support
- Break-even and profitability analysis
As my business grows, can the CFO services be scaled up?
- Fundraising advisory (Series A, B, etc.)
- Advanced tax structuring and planning
- International taxation and FEMA compliance (for global expansion)
What makes Setindiabiz’s Virtual CFO service different from hiring an in-house CFO or using other accounting firms?
- Cost-Effective Financial Management: Get CFO-level expertise without the expense of a full-time hire.
- Industry-Specific Insights: Customized financial solutions tailored for startups & SMEs.
- End-to-End Compliance Management: GST, TDS, Income Tax, Companies Act – all handled seamlessly.
- Scalability: Start with basic accounting, then expand services as your business grows.
- Technology-Driven Approach: We use cloud-based accounting solutions, automation, and AI-driven insights.

