Overview : One of the most frequently asked questions in corporate compliance relates to whether Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) enjoy the same flexibility as companies when maintaining books of account at alternative locations. While Section 128 of the Companies Act 2013 allows companies to file Form AOC-5 and designate different addresses for book maintenance, the LLP Act 2008 takes an entirely different approach. This comprehensive guide explores the stark differences between these two business structures and answers whether LLPs can leverage similar provisions for address designation.
What is Form AOC-5?
Form AOC-5 is a crucial compliance document under Section 128 of the Companies Act 2013 that allows companies to designate an alternative address for maintaining their books of account. When filed with the Registrar of Companies (ROC), this form enables businesses to keep their financial records at a location different from their registered office address.
Key Requirements for Form AOC-5 Filing
Companies must fulfil several critical requirements when filing Form AOC-5. First, the board of directors must pass a resolution authorising the alternative location for book maintenance, establishing formal approval for the change. Following this board authorisation, companies must file Form AOC-5 within seven days of the board resolution to ensure timeline compliance.
List of Documentation for AOC-5 (Post-2023 Amendment)
- GPS coordinates (latitude and longitude) of the alternative location
- Photographs of the building’s exterior and interior
- Details of local police station jurisdiction
- Images showing at least one director or KMP at the location
SAMPLE BOARD RESOLUTION FOR FORM AOC-5 FILING BOARD RESOLUTION
CERTIFIED TRUE COPY OF THE RESOLUTION PASSED AT THE MEETING OF THE BOARD OF DIRECTORS OF [COMPANY NAME] HELD ON [DATE] AT [REGISTERED OFFICE ADDRESS]“RESOLVED THAT pursuant to the provisions of Section 128(1) and other applicable provisions of the Companies Act, 2013 and the rules made thereunder, consent of the Board be and is hereby accorded to keep the books of account and other relevant papers of the company at the following address: [Complete New Address Where Books Are to Be Maintained]”
RESOLVED FURTHER THAT Mr./Ms. [Name of Authorized Signatory], [Designation], be and is hereby authorised to file the necessary e-Form AOC-5 with the Registrar of Companies and to do all such acts, deeds, matters and things as may be deemed necessary or expedient to give effect to this resolution.
RESOLVED FURTHER THAT a certified true copy of the resolution be provided to any concerned authority or party as and when required.
Public Disclosure Impact : Once Form AOC-5 is filed and accepted, the alternative address becomes part of the company’s master data, visible on the MCA portal at www.mca.gov.in. This means stakeholders, creditors, and the general public can access information about where the company
LLP Book Maintenance: A Restrictive Framework
The definitive answer is NO—LLPS do not have a provision equivalent to Form AOC-5 under the Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008. Section 34 of the LLP Act 2008, read with Rule 24 of the LLP Rules 2009, explicitly mandates that every LLP maintain its books of account at its registered office.
Legal Framework Governing LLP Book Maintenance
Section 34 of the LLP Act 2008 establishes the fundamental obligation for LLPs to maintain proper books of account. The provision requires books to be maintained regularly, using the double-entry system, and kept at the registered office address.
Rule 24 of LLP Rules 2009 : This rule mandates explicitly that books of account shall be kept at the registered office of the limited liability partnership. There are no provisions for alternative locations or any form similar to AOC-5.
What About Form 12 for LLPs?
While LLPs can file Form 12 to declare an “other address for service of documents,” this provision serves an entirely different purpose. This alternate address is strictly for communication purposes, such as receiving notices and correspondence from the MCA and other stakeholders. Legal experts clarify that Form 12 cannot be interpreted as an authorisation for maintaining official books of account at an alternative address.
Illustrative MCA Master Data
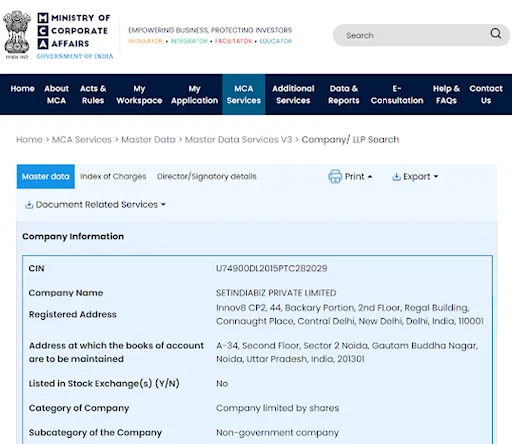
MCA Master Data: Transparency Differences
- Company Information Display (MCA Master Data) : When companies file Form AOC-5, the MCA master data displays, in addition to name, cin, date of incorporation, and other information, the Registered office address, Alternative address for books of account maintenance, and Complete details with verification status.
- LLP Information Limitations (MCA Master Data) : LLP master data on the MCA portal shows only basic information, including registered office address, partner details, and filing status. There are no provisions for displaying alternative book maintenance addresses because such alternatives don’t exist under LLP law.
Comparative Analysis: Companies vs LLPs
| No | Aspect | Companies (Section 128) | LLPs (Section 34 & Rule 24) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alternative Address Permission | ✅ Yes, through Form AOC-5 | ❌ No provision available |
| 2 | Required Documentation | Board resolution + Form AOC-5 | Not applicable |
| 3 | GPS Coordinates Required | ✅ Yes (post-2023 amendment) | ❌ Not applicable |
| 4 | Public Disclosure | ✅ Both registered office and alternative address | ✅ Only registered office |
| 5 | Filing Timeline | 7 days from board resolution | Not applicable |
| 6 | Photographs Required | ✅ Yes (building + interior + personnel) | ❌ Not required |
| 7 | MCA Master Data Display | Shows both addresses | Shows only registered office |
| 8 | Communication Address | Separate provision via other forms | Form 12 (communication only) |
| 9 | Compliance Burden | High (detailed documentation) | Low (single location only) |
| 10 | Flexibility | High operational flexibility | Limited to the registered office |
Compliance Implications and Penalties
Companies violating Section 128 face fines ranging from Rs. 50,000 to Rs. 5,00,000, with individual liability for managing directors, whole-time directors, and other key personnel. LLPs failing to maintain proper books face fines from Rs. 25,000 to Rs. 5,00,000 for the entity and Rs. 10,000 to Rs. 1,00,000 for each designated partner. However, compliance is theoretically simpler since books must be maintained only at the registered office.
Conclusion
The absence of a Form AOC-5 equivalent for LLPs represents a fundamental regulatory difference from companies. While companies enjoy operational flexibility through alternative book maintenance addresses with public MCA disclosure, LLPs remain restricted to their registered offices under Section 34. This distinction significantly impacts entity selection decisions – companies suit businesses requiring operational flexibility, while LLPs benefit those prioritising simplified compliance and privacy. Understanding these differences is crucial for informed business structure decisions and long-term compliance success.