What is the Private Security Agencies (Regulation) Act 2005? – Meaning, Key Concepts and Features
In a world where security concerns are paramount now more than ever, the Private Security Agencies (Regulation) Act 2005, better known as the PSARA Act, stands tall as a pillar of assurance and protection for businesses and individuals alike. Enacted by the Government of India, the PSARA Act plays a vital role in overseeing the functioning of private security agencies to uphold the safety and welfare of the public at large.
Designed with a clear objective in mind, the PSARA Act seeks to establish a robust regulatory framework that governs the operations of private security agencies across the nation. With the private security sector witnessing a rapid growth in India owing to growing security concerns, this legislation assumes even greater significance as it sets forth specific standards for security agencies and their services, mandates licensing requirements, and enforces crucial legal provisions to maintain a high level of professionalism and competence within the industry.
Understanding the PSARA Act of 2005
In response to the growing importance of private security agencies and the need to ensure the safety and well-being of citizens, the Government of India introduced the Private Security Agencies (Regulation) Act 2005, commonly known as the PSARA Act. This significant piece of legislation serves as a critical milestone in the regulation and oversight of private security services across the nation.
At its core, the PSARA Act aims to establish a comprehensive regulatory framework that governs the functioning of private security agencies. Prior to its enactment, the private security sector witnessed a proliferation of agencies, with varying levels of professionalism, standards, and reliability. The absence of a standardized regulatory system led to concerns about the quality of services provided by some agencies, potentially jeopardizing public safety and security. So, the act was introduced with a prescribed set of objectives to overcome this challenge, as discussed in the further section.
Objectives of the PSARA Act
Although the major objective of PSARA Act is to regulate Private Security Agencies, there is more to it than what appears. Let’s explore the major objectives for the introduction of PSARA Act in India and how these objectives have paved the way for a robust private security sector in the midst of new and emerging security challenges.
- Regulating Private Security Agencies: The Act sets out guidelines and procedures for the operation of private security agencies, including requirements for obtaining licenses and adherence to specific code of conduct.
- Safeguarding Public Interests: By implementing stringent eligibility criteria, background checks, and training requirements for private security guards, the Act aims to safeguard the interests of the public and instill confidence in the services provided by private security agencies.
- Ensuring Professionalism and Competence among Security Agencies: The Act emphasizes the necessity of employing well-trained and qualified security personnel, thereby enhancing the overall professionalism and competence of the private security industry.
- Creating a Competent Authority for administration: The Act designates a Controlling Authority responsible for overseeing the implementation of its provisions and ensuring compliance by private security agencies.
- Establishing Penalties for Violations and Non-Adherence: To maintain accountability and adherence to the Act’s guidelines, it outlines penalties and consequences for agencies found in violation of its provisions.
Key Concepts and Definitions Under the PSARA Act
The Private Security Agencies (Regulation) Act 2005 lays the groundwork for a well-organized and standardized private security industry in India. With a focus on public safety and security, the Act establishes essential concepts and definitions that govern the operations of private security agencies. Understanding these key concepts is crucial for these agencies to ensure complete compliance with the provisions of the Act. Let’s delve into the key concepts and definitions under the PSARA Act.
| Key Terms | Concept & Definition |
|---|---|
| Private Security Agency | A Private Security Agency (PSA) refers to any proprietor or business entity engaged in providing private security services to individuals or establishments for consideration. These agencies play a vital role in the private security industry, offering services such as manned guarding, electronic surveillance, and security consulting solutions. |
| Controlling Authority | The Controlling Authority, as designated by the PSARA Act, is responsible for granting, renewing, suspending, or canceling licenses of private security agencies. This authority ensures that private security agencies operate within the legal framework and comply with the PSARA Act’s regulations, thus safeguarding public interests. |
| Private Security Guard | Private Security Guards are individuals employed or engaged by private security agencies to deliver security services to clients. They are at the forefront of private security operations, responsible for ensuring the safety and protection of individuals and assets. |
| PSARA License | A PSARA License is a mandatory authorization granted by the Controlling Authority to private security agencies, enabling them to legally operate and offer security services in India. This license ensures that only legitimate and competent agencies provide security services, maintaining professionalism and standardization in the industry. |
| Antecedent Verification | Antecedent verification involves a comprehensive check of the qualifications, criminal history, and past conduct of individuals employed as private security guards. This process is a critical step in the licensing procedure, ensuring that security guards are trustworthy and suitable for their roles. Antecedent Verification is conducted by the local police authorities and the Controlling Authorities. |
| Security Training Institute and MOU | Under the PSARA Act, private security agencies are required to associate with a Security Training Institute recognized by the Controlling Authority and sign a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) to provide adequate training to their security guards and supervisors. This training equips security guards with the necessary knowledge and expertise to effectively handle various security challenges and emergency situations they encounter in the line of their duty. |
Key Features of the PSARA Act, 2005
The Private Security Agencies (Regulation) Act 2005 encompasses several key features that form the backbone of its regulatory framework. These features play a vital role in governing private security agencies, ensuring their operations are conducted professionally, ethically, and in line with public interests. Let’s explore the significant features of the PSARA Act to understand its objective more clearly.
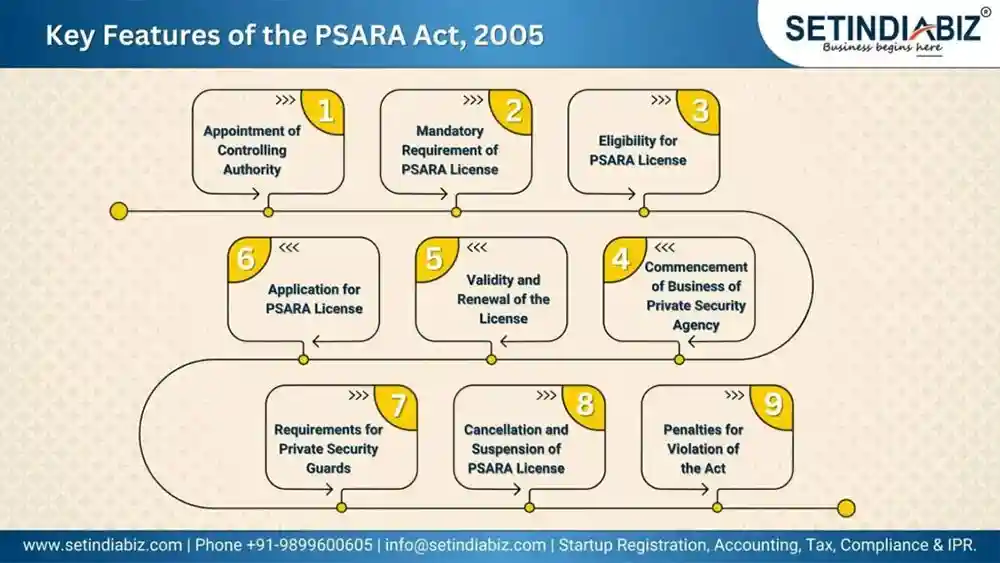
- Appointment of Controlling Authority: The Act designates a Controlling Authority responsible for overseeing the implementation of its provisions. This Authority plays a pivotal role in granting, renewing, suspending, or canceling licenses of private security agencies within a specific area of operation. It ensures that agencies comply with the Act’s guidelines, promoting public safety and security.
- Mandatory Requirement of PSARA License: One of the foremost features of the Act is the compulsory requirement for all private security agencies to obtain a PSARA License. This license serves as authorization to operate legally, and without it, agencies are not permitted to provide security services.
- Eligibility for PSARA License: To be eligible for a PSARA License, private security agencies must meet specific criteria, including financial viability, infrastructure capabilities, and adherence to the Act’s guidelines. Background verification of directors and shareholders/partners is also mandatory to ensure the agency’s credibility.
- Application for PSARA License: The Act outlines a detailed process for agencies to apply for a PSARA License. Applicants must submit required documents and information to the Controlling Authority, which then evaluates their suitability for the license.
- Validity and Renewal of the License: Once granted, a PSARA License remains valid for a specified duration only. Agencies must ensure timely renewal before the expiry to maintain their legal status. Renewal applications undergo a similar evaluation process as the original application.
- Commencement of Business of Private Security Agency: The Act specifies regulations regarding the commencement of operations by a private security agency six months after obtaining the license. Agencies are permitted to provide services only after obtaining a valid PSARA License.
- Requirements for Private Security Guards: Private security agencies must employ individuals who meet the Act’s criteria as security guards. The Act mandates antecedent verification of the guards and enforces training requirements for them to ensure reliability over the services they provide.
- Cancellation and Suspension of PSARA License: In cases of non-compliance or violation of the Act’s provisions, the Controlling Authority is empowered to suspend or cancel the PSARA License. This measure helps maintain the integrity of the private security industry and ensures that the agencies operating thereunder have appropriate standards.
- Penalties for Violation of the Act: The Act prescribes penalties and consequences for private security agencies found in violation of its provisions. Penalties may range from fines to suspension or cancellation of the PSARA License, depending on the severity of the violation.
Conclusion
The Private Security Agencies (Regulation) Act 2005, or the PSARA Act, has played a pivotal role in shaping the private security industry in India. By establishing a robust regulatory framework for these agencies and emphasizing professionalism, competence, and accountability at their end, the Act ensures standardized and reliable security services for individuals and businesses in India. With its focus on public safety and security, the Act instills trust in private security agencies, contributing to a safer and more secure environment overall. As the Act continues to evolve through regular progressive amendments, its impact on the private security landscape remains a significant aspect of ensuring the well-being of individuals and establishments across the nation.
FAQ's
The PSARA Act’s main objective is to regulate private security agencies in India and ensure the standardized operation of these agencies to enhance public safety and security.
Yes, the PSARA Act makes it compulsory for all private security agencies to obtain a valid PSARA license before they can legally operate and provide security services.
Operating without a valid PSARA license is illegal and can lead to severe penalties, including fines up to Rs.25,000, suspension, or cancellation of the license, or an imprisonment for a duration extending to 1 year. It is essential for private security agencies to comply with the licensing requirements to avoid such consequences.
Yes, the Controlling Authority has the power to suspend or cancel a private security agency’s license if the agency is found to be in violation of the Act’s provisions or engaged in unethical practices.
The Controlling Authority is responsible for overseeing the implementation of the Act’s provisions and ensuring that private security agencies adhere to the guidelines and regulations, safeguarding public interests. It is also responsible for granting the PSARA license to applicant agencies and proprietors.
Author Bio

Editorial Team | in
Setindiabiz Editorial Team is a multidisciplinary collective of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Advocates offering authoritative insights on India’s regulatory and business landscape. With decades of experience in compliance, taxation, and advisory, they empower entrepreneurs and enterprises to make informed decisions.
