What Is Private Security Agency License (PSARA)?
PSARA license is one of the most significant requirements under the PSARA Act to operate a Private Security Agency in India. In this blog, we have explained the concept of PSARA License elaborately, and shared the details of its prerequisites, application process, and activities to be completed post-grant the license for your complete and comprehensive understanding.
Private Security Agencies are organisations involved in providing security services including training of security guards. The operation of private security agencies is governed by The Private Security Agencies Regulation Act, 2005, in short called as PSARA. With rising concerns about crime and terrorism, the demand for private security services is increasing steadily among the public to protect themselves against different types of crime. This has led to an increase in Private Security Agencies. Learn How to Apply for PSARA License.
Police of Law and Order is a state subject under the constitutional pattern of lawmaking, however, as the national security is in the Central List, hence Indian parliament has passed a law to regulate the formation and operation of private security agencies in India and also conferred the state governments to appoint controlling authorities and frame rules for the smooth functioning of the private security business in India. Accordingly, no person can start the business of providing security guards directly or indirectly without holding a valid PSARA License.
What is PSARA Full Form and Meaning
The full form of PSARA is the “Private Security Agencies Regulation Act.” Enacted in 2005 by the Government of India, this Act aims to regulate and govern the functioning of private security agencies across the country. Its primary objective is to ensure the professionalization and standardization of security services provided by these agencies.
Under the PSARA Act, individuals or entities intending to operate as private security agencies must obtain the mandatory PSARA License. This license serves as a legal authorization that validates their capability to offer security services to clients. By enforcing specific eligibility criteria, conducting antecedent verification, and setting guidelines for training and compliance, the PSARA Act plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of private security services in India.
What is PSARA License?
PSARA License is a mandatory requirement for all Private Security Agencies in India, under the PSARA Act of 2005 as discussed above. Section 4 of the Act states that “No person shall carry on or commence the business of a private security agency, unless he holds a license issued under this Act”. The license helps the Government govern and regulate the functioning of private security agencies in India and ensure that they adhere to specific standards and guidelines set forth to maintain the quality and credibility of their services. PSARA License is granted by the jurisdictional Controlling Authority of the place where the agency is located. This means that the validity of the license is limited territorially, and to operate at multiple locations, multiple PSARA licenses have to be obtained. Additionally, if an agency seeks to provide its services beyond Indian boundaries, it cannot do so without obtaining prior permission from the Controlling Authority and the Central Government.
Who is the Controlling Authority for Granting PSARA License?
The Central Government mandates every state government, to appoint as a Controlling Authority an officer who is not lower than the rank of Joint Secretary, to implement the provisions of the PSARA Act in the region. The powers of the Controlling Authority are limited by the jurisdiction he is incharge of, which means that he is only responsible for controlling private security agencies within a specific area of operation. Following are the general duties of the controlling authority appointed under PSARA:
- Issuance & Renewal of the PSARA license
- Regulation of the operations of private security agencies.
- Recognition of Security Training Institutes to train Private Security Guards
- Other functions as prescribed by the PSARA Act.
Prerequisites & Eligibility For PSARA License
Before venturing into the private security industry in India, both applicant Private Security Agencies or Individual proprietor must navigate a prescribed set of prerequisites and eligibility criteria mandated by the Private Security Agencies Regulation Act (PSARA). These requirements serve as crucial benchmarks, ensuring the credibility, professionalism, and adherence to the law of those seeking to operate in this vital sector. Let’s delve into the key prerequisites that aspiring security entities must fulfill to obtain the coveted PSARA License:
- Select the Right Type of Business Structure: To secure a PSARA License, the applicant agency must either be a company, a Limited Liability Partnership, a Partnership Firm, or a Sole Proprietorship.
- Select a Proper Name for the Agency: If you’re about to run a Private Security Agency, its name must be appropriate. It must not show patronage of the Government. Also, it must be suffixed by words like “Security Agency”, “Security Services”, or something similar, which aptly conveys its business activities,
- Incorporate/ Register your business to mark its legal existence: Before you apply for the PSARA License, your business must be constituted and incorporated by following the due process under law. For this you need to draft necessary constitutional documents, like MOA and AOA for a company, LLP agreement for LLP, Partnership Deed for a firm, and so on. Also, you need to apply for their incorporation with the appropriate authority and obtain the Incorporation Certificate.
- Antecedent Verification of Owners and Key Officers of the Agency: Owners, Directors or principal officers of the agency must be Indian citizens, financially sound, and free from any legal convictions.To ensure this, thorough verifications are conducted by the Controlling Authority and the local police authorities.
- Prepare the necessary documents for PSARA license: The last yet most important prerequisite to fulfill before the PSARA license application process is the collection and preparation of all the necessary documents. These include the documents of the key managerial persons, the documents of the agency’s legal constitution and incorporation, the documents of its premises, and documents related to other regulatory and tax registrations like the EPF, ESI, GST and so on.
Stages Of PSARA License Application
The process of obtaining a PSARA License is a significant undertaking for private security agencies in India. Governed by the Private Security Agencies Regulation Act (PSARA), this license serves as a crucial authorization, granting security agencies the legal right to provide their services in a designated territory. The application process involves multiple stages, each playing a pivotal role in determining the agency’s eligibility and adherence to prescribed standards.
Let’s delve deeper into the stages of the PSARA License application process:
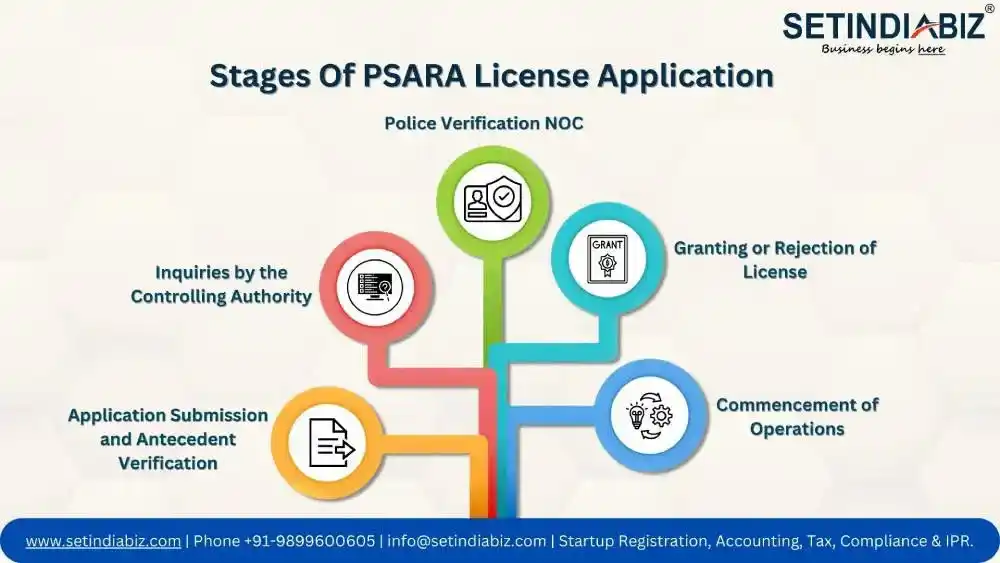
- Application Submission and Antecedent Verification: Private security agencies initiate the process by submitting a well-prepared application to the designated controlling authority of the respective state. The application contains essential details about the agency, its directors, and the proposed geographical area of operation.
- Inquiries by the Controlling Authority: Upon receiving the application, the controlling authority conducts in-depth inquiries to assess various aspects of the agency, its promoters, and its key managerial persons. They might inquire about their individual experience in operating security agencies, any special qualifications or skills that could contribute to the agency’s operations, and overall eligibility for obtaining the PSARA License.
- Police Verification NOC: The Police Verification No Objection Certificate holds significant importance in the PSARA License application process. It involves a thorough background check by relevant law enforcement authorities to ensure the applicants have no pending criminal cases and are of good character. Additionally, the police verifies if the applicants or their owners have any involvement in activities detrimental to national security or public order. The certificate is granted only after assuring the applicants’ integrity and suitability to operate a private security agency, and only upon receipt of the Police Verification NOC does the controlling authority proceed to grant the license, underscoring its crucial role in the evaluation and approval of PSARA License applications.
- Granting or Rejection of License: Based on the information obtained and the outcome of the verification process, the controlling authority decides whether to grant the PSARA License to the agency or reject the application by providing appropriate reasons for such decision. The PSARA license is typically granted within 60 days from the date of a complete application submission.
- Commencement of Operations: The PSARA License can be applied for a specific district, multiple districts, or the entire state, depending on the agency’s intended area of operation. The government fee for the application varies based on the number of districts applied for. Once the PSARA License is granted, the security agency must commence its business operations within six months from the date of issuance.
Activities Post-Grant of PSARA License
Once a private security agency has successfully obtained the PSARA License, a series of vital activities must be undertaken to ensure compliance with the provisions of the Private Security Agencies Regulation Act (PSARA). These activities serve as the cornerstone for establishing a reputable and trustworthy security agency, and they are essential for operating within the boundaries of the law while upholding the highest standards of professionalism.
- Commence Operations Within 6 Months: After obtaining the PSARA License, the agency must begin operations within six months, setting up the office premises and deploying security guards for client services.
- Employ Security Guards under Strict Standards: Private security agencies must adhere to strict qualifying standards (link later) when hiring security guards, ensuring they are physically fit and capable of carrying out their duties effectively.
- Engage Supervisors for Security Guards: Within sixty days of obtaining the license, supervisors must be employed to oversee security guards’ work, maintaining a ratio of one supervisor for every fifteen guards.
- Give Preference to Ex-Servicemen While Hiring: When hiring supervisors, preference is given to those with a minimum of three years of experience in the Army, Navy, Air Force, or State Police.
- Conduct Comprehensive Character and Antecedent Verification: Thorough verification of character and antecedents is mandatory for security guards and supervisors before their employment.
- Conduct Training of Security Guards: Security guards must undergo training as per the syllabus outlined by the Controlling Authority, covering various aspects of security services.
- Maintain Essential Registers: Private security agencies are required to maintain registers containing critical information about management personnel, security guards, supervisors, and clients.
- Issue Photo Identity Cards to Guards & Supervisors: Identity cards with photographs must be issued to all security guards and supervisors, serving as a means of identification and verification of credentials.
Conclusion
The Private Security Agencies Regulation Act (PSARA) stands as a crucial framework governing the operation of private security agencies in India. Through its stringent eligibility criteria, antecedent verification, and mandatory PSARA License, the Act ensures the professionalization and standardization of security services. Aspiring agencies must meet the prerequisites and adhere to compliance measures, such as employing trained security guards and engaging qualified supervisors. By maintaining high standards and fulfilling the legal obligations, private security agencies can earn the trust of clients and contribute significantly to safeguarding public interests and enhancing safety across the nation. As the private security industry continues to play a vital role in protecting individuals and establishments, staying well-informed about the PSARA Act's provisions becomes paramount in ensuring a secure and lawful environment.
FAQ's
Private security agencies providing security services in India need a PSARA License as per Section 4 of the PSARA Act. Not obtaining the license is an offense under the Act and can be penalized with a fine of up to Rs.25,000 or an imprisonment of a term up to 1 year or both.
For agencies: Must be registered as a private limited company, limited liability partnership, partnership firm, or sole proprietorship. Directors/principal officers must be Indian citizens with no criminal records. For individuals: Indian nationality with no criminal convictions related to company management or offenses carrying a minimum two-year imprisonment.
Antecedent verification involves background checks to ensure applicants have a clean legal and financial record and are suitable for providing security services.
PSARA License is obtained after completing various stages of application. The process usually takes 60 days from the date of submitting a complete application.
Post-license, agencies must commence operations within six months, employ qualified security guards, engage adequate supervisors, conduct character and antecedent verification of employed personnels, provide security guard training, maintain essential registers, and issue photo identity cards to guards and supervisors.
Author Bio

Editorial Team | in
Setindiabiz Editorial Team is a multidisciplinary collective of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Advocates offering authoritative insights on India’s regulatory and business landscape. With decades of experience in compliance, taxation, and advisory, they empower entrepreneurs and enterprises to make informed decisions.
