Provisional Patent Application – The Complete Guide
Overview : Read this complete guide on Provisional Patent Application India covering every aspect of the process, from eligibility requirements to the detailed steps of filing and documents required for submission. We have explained essential concepts like Patent Specification and Complete Patent Filing as well, to give you a clearer understanding. Explore the crucial benefits, validity, and cost of Provisional Patent in India. Ask any further questions in the comments below or directly contact our experts!
A provisional patent application India serves as an initial step towards safeguarding inventive ideas, offering inventors temporary protection while they refine their inventions or seek potential investors. Essentially, it provides a placeholder in the patent application process, establishing a priority date for the invention. This priority is crucial, especially in competitive industries, as it secures the inventor’s rights amidst a race to innovation. Through the lens of intellectual property rights (IPR) protection, the significance of a provisional patent cannot be overstated. It not only shields inventive concepts but also offers inventors the flexibility and time needed to develop their ideas further, potentially paving the way for future commercial success.
Why is Patent Application Important?
Patent applications are filed primarily to secure exclusive intellectual property rights over inventions or innovations. By obtaining a patent, inventors gain legal protection, preventing others from making, using, selling, or importing their invention without permission. This exclusivity incentivizes innovation by allowing inventors to reap the rewards of their efforts, whether through commercialization, licensing agreements, or other means. Moreover, patents serve as valuable assets, bolstering a company’s competitive edge and potentially increasing its market share and profitability.
Beyond individual benefits, patent applications also contribute to societal progress by promoting knowledge sharing and technological advancement. The patent system encourages inventors to disclose their inventions in detail, thereby adding to the collective pool of human knowledge. This disclosure facilitates further innovation by enabling others to build upon existing ideas, leading to the development of new technologies and solutions to pressing challenges. In essence, patent applications serve as a cornerstone of the innovation ecosystem, fostering creativity, driving economic growth, and enhancing overall societal welfare.
Types of Patent Applications
Before seeking patent protection for your inventions, understanding the types of patent applications becomes imperative. The Indian patent laws recognize two primary types of patent applications, based on their purpose and validity of patent granted. These include the Provisional Patent and Complete Patent Applications. Let’s distinguish between the two.
Provisional Patent Application
Filing Provisional Patent applications serve as crucial initial steps for inventors and businesses alike. Acting as a temporary placeholder, these applications provide inventors with a filing date and establish a priority date for their invention. This priority date is instrumental in securing their rights amidst a competitive innovation landscape. Moreover, provisional patents offer inventors the flexibility to continue refining their inventions or exploring potential commercialization opportunities while maintaining priority over their intellectual property.
Complete Patent Application
Complete patent applications, represent formal submissions to the Indian patent office for examination and potential grant of a patent. Unlike provisional applications, complete patent applications require formal claims and a detailed description of the invention, including any necessary drawings. In the context of Patent Application India, these submissions undergo rigorous examination processes to assess the novelty, non-obviousness, and utility of the invention. Upon successful examination and fulfillment of patentability criteria, a patent may be granted, providing inventors with exclusive rights to their inventions within India for a specified period.
Key Differences between Provisional Patent & Complete Patent Applications
| Parameters | Provisional Patent Application | Complete Patent Application |
| Filing Purpose | Acts as a temporary placeholder | Formal submission for examination and potential grant |
| Filing Requirements | Less formal, no formal claims required | Requires formal claims and detailed description |
| Priority Date | Establishes priority date for the invention | Maintains priority date from provisional application |
| Duration of Protection | Provides temporary protection for 12 months | Grants exclusive rights for up to 20 years |
| Examination and Grant Process | Does not undergo examination | Subject to rigorous examination for patentability |
| Claims | No formal claims required | Formal claims necessary for defining patent scope |
| Cost | Typically lower filing fees | Generally higher filing and examination fees |
| Drawings and Description | Optional but recommended for clarity | Required, including detailed description and drawings |
What is a Provisional Patent Application India?
A provisional patent application serves as a strategic tool for inventors, particularly during the research and development (R&D) phase of their inventions. Its primary function is to secure the novelty of the invention and prevent any inadvertent disclosure of sensitive information while the invention is still in the developmental stages. As per Section 9 of the Indian Patent Act, 1970, filing a patent application with a provisional specification allows inventors to establish the priority date of their invention, providing a safeguard against information leakage.
The immediate advantage of applying for provisional patent lies in its ability to protect the invention from potential disclosure risks, thereby preserving the inventor’s intellectual property rights. By submitting a provisional specification, inventors can secure a filing date for their invention without the need for formal claims or a detailed description, thus streamlining the initial filing process. However, it’s important to note that while provisional applications offer temporary protection for a period of 12 months, inventors must follow up by filing a complete patent specification within this timeframe.
In situations where the invention is fully developed and ready for patenting, inventors are advised to file an application with a complete specification to expedite the patenting process. The complete specification provides a comprehensive description of the invention, including formal claims, and must be submitted within 12 months of filing the provisional application to maintain priority rights.
Is Filing a Provisional Patent Application Mandatory?
Filing a Provisional Patent Application is not mandatory; it’s an option available to inventors or applicants. Alternatively, applicants can choose to submit the patent application with a complete specification right from the outset, provided the invention is fully developed and ready for patenting. However, opting for a provisional application can be an excellent strategy, especially if the invention is still in the research and development stage, as it helps maintain the secrecy of the invention.
It’s important to note that filing a provisional application doesn’t mean providing rough or incomplete details about the invention. On the contrary, the provisional application should clearly define the scope of the invention, laying a solid foundation for subsequent patent filings. The complete specification submitted later should closely align with the provisional specifications, as the examiner considers both documents during the examination process. Therefore, drafting a comprehensive and well-defined provisional specification is crucial.
It’s worth emphasizing that failing to file the complete specification within 12 months of submitting the patent application with the provisional specification may result in the application being deemed abandoned. This underscores the importance of timely conversion of provisional applications into complete specifications to maintain priority rights and preserve the inventor’s intellectual property.
Eligibility and Requirements For Provisional Patent
Determining eligibility for provisional patent is a critical step in the patent grant process. While provisional patents offer several benefits, not all inventions may qualify for this initial form of protection. The criterias are based on the originality of invention, its utility, scope, description, and inventorship claims. Here are the key factors to consider when assessing eligibility:
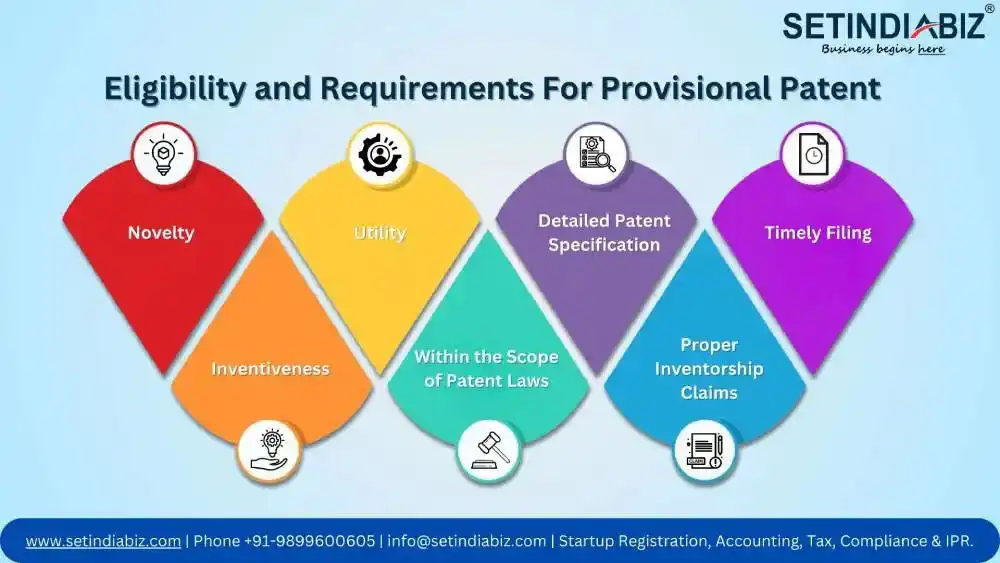
- Novelty: Novelty refers to the requirement that the invention must be new and not disclosed to the public before the filing date of the provisional application. Any prior public disclosure, such as publications, presentations, or offers for sale, can jeopardize the novelty of the invention.
- Inventiveness: Inventiveness, also known as non-obviousness, refers to the requirement that the invention should involve an inventive step, meaning it should not be obvious to someone skilled in the relevant field of technology. The invention should represent a significant departure from what is already known in the field.
- Utility: Utility refers to the requirement that the invention must have a practical utility, meaning it should be capable of being used or applied in some way to provide a tangible benefit. The invention should serve a useful purpose or solve a specific problem.
- Within the Scope of Patent Laws: Provisional patents can be obtained for various types of inventions, including products, processes, machines, compositions of matter, or improvements thereof. The subject matter of the invention should fall within the scope of patentable subject matter as defined by patent laws.
- Detailed Patent Specification: Provisional specification must provide an enabling disclosure. This means that the specification should contain enough detail to allow a person skilled in the relevant field to understand and replicate the invention without undue experimentation. The description should be clear, concise, and sufficiently comprehensive to enable others to practice the invention.
- Proper Inventorship Claims: The inventorship of the provisional patent must accurately mentioned in the application and reflect those individuals who have made a significant contribution to the conception of the invention. It’s essential to identify all inventors involved in the creation of the invention and properly attribute their contributions.
- Timely Filing: To maintain eligibility for provisional patent protection, the application must be filed within one year of any public disclosure of the invention. Public disclosures include publications, presentations, demonstrations, or offers for sale. Filing within this timeframe is crucial to preserving the novelty of the invention and securing priority rights.
Documents Required for Provisional Patent Application
While securing provisional patent protection for an invention, the preparation of a comprehensive patent specification and the submission of requisite documents are paramount. These documents not only serve as the foundation for the grant of patent but also play a crucial role in determining its scope, and field of use. Here’s an overview of the essential documents and components required for filing a patent application:
Forms Required:
- Form 1: Prescribed application form for filing a patent.
- Form 2: Provisional specification form.
- Form 5: Declaration to be signed by the inventor.
- Form 26: Power of attorney for patent attorney/agent.
- Form 3: Applicable for foreign applicants only.
- Prescribed government filing fee.
Contents of the Provisional Specification:
- Title of the Invention: A concise and precise title framing the essence of the invention.
- Area or Field of the Invention: Clear description of the technological field to aid patent examiners.
- Background of Invention & Prior Art: Explanation of prior art and distinction from existing technologies.
- Economic Advantages of the Invention: Demonstration of commercial value and economic advancement.
- Statement of Invention: Description of the innovative features distinguishing the invention.
- Summary of Invention: Overall depiction outlining the invention’s key aspects.
- Brief Description of Accompanying Drawings: Optional for provisional specification.
- Detailed Description of the Invention with Drawing/Examples: Optional for provisional specification.
- Claim(s): Filed with complete specification, essential for defining the scope of the invention.
- Abstract: Succinct overview reflecting the technical field, problems addressed, and solutions offered.
Process of Filing Provisional Patent Application
Navigating the process of applying for a provisional patent requires meticulous attention to detail and strict adherence to specific procedures. Each step in the process plays a crucial role in determining the success of the patent application and ultimately securing intellectual property rights. Here’s a comprehensive step-by-step guide to assist you in successfully filing a provisional application or patent registration, ensuring that your innovative ideas are protected effectively and legally.
Step 1: Conduct Preliminary Research:
Before initiating the application process, conduct thorough research to ensure that your invention is novel and inventive. Review existing patents, literature, and databases to assess the novelty of your invention and its potential patentability. Conducting a thorough patent search will enhance the chance of your application getting approved.
Step 2: Draft the Patent Description and Specification:
Draft a detailed description of your invention, including its features, functionalities, and any unique aspects. Be sure to include drawings or diagrams to illustrate the invention’s structure and operation effectively. Prepare the provisional specification document, outlining the technical details of your invention. Clearly describe the invention’s novelty, inventive step, and practical utility. Ensure that the specification meets the enablement requirement, providing sufficient detail for someone skilled in the field to replicate the invention.
Step 3: Submit Provisional Patent Forms:
Fill out the required application forms, including Form 1 for the patent application and Form 2 for the provisional specification. Provide accurate information and ensure that all necessary documents are attached. File the completed application forms and provisional specification with the appropriate patent office. Pay the requisite filing fees and any associated charges to complete the application process.
Step 4: Follow-Up with Complete Specification:
Within 12 months of filing the provisional application, prepare and file the complete specification and application. The complete specification should build upon the provisional specification and include formal claims. Once the complete application is approved, the applicant receives patent protection for 20 years. However, this term is neither extendable nor renewable. After the expiry of the Complete Patent, the invention enters the public domain.
Cost and Validity of Provisional Patent Filing
Understanding the cost implications and validity period of provisional patents is essential for inventors seeking to protect their intellectual property. The overall cost depends on the factors such as the government fees, professional fees, and other miscellaneous expenses. As far as the validity is concerned, it only extends until you file the complete application. Read the details below:
Cost of Provisional Patent
- Government Filing Fee: The cost of filing a provisional patent application with a standard patent specification upto 30 pages is Rs.1,600 (Rs.1,750 for offline filing), if the applicant is a startup, natural person or a small entity. For others, the applicable fee is Rs.8,000 (Rs.8,800 for offline filing). However, if the specification drafted exceeds 30 pages, the charges will increase by Rs.160 per sheet for natural persons, startups, and small entities (Rs.800 per sheet for offline filing), whereas Rs. 180 for others (Rs.880 for offline filing).
- Professional Fees: Inventors may incur professional fees if they choose to seek assistance from patent attorneys or agents in preparing and filing the application. These fees can vary based on the expertise and experience of the professionals hired.
- Additional Expenses: There may be additional expenses associated with drafting the provisional specification, conducting prior art searches, and preparing any necessary drawings or diagrams.
Validity of Provisional Patent
A provisional patent provides inventors with temporary protection for their invention, establishing a priority date for the filing. This priority date is crucial for determining the novelty of the invention and securing priority rights. The validity period of a provisional patent is 12 months from the filing date. Within this timeframe, inventors must file a complete patent application to maintain priority rights and convert the provisional application into a non-provisional patent. It’s important to note that the validity period of a provisional patent cannot be extended beyond the 12-month timeframe. Failing to file a complete patent application within this period may result in the abandonment of the provisional application, jeopardizing the inventor’s priority rights.
Key Benefits of Obtaining a Provisional Patent
Filing a provisional patent application offers several key benefits for inventors and businesses looking to protect their intellectual property and secure priority rights for their innovations. Here are some of the key advantages of obtaining a provisional patent:
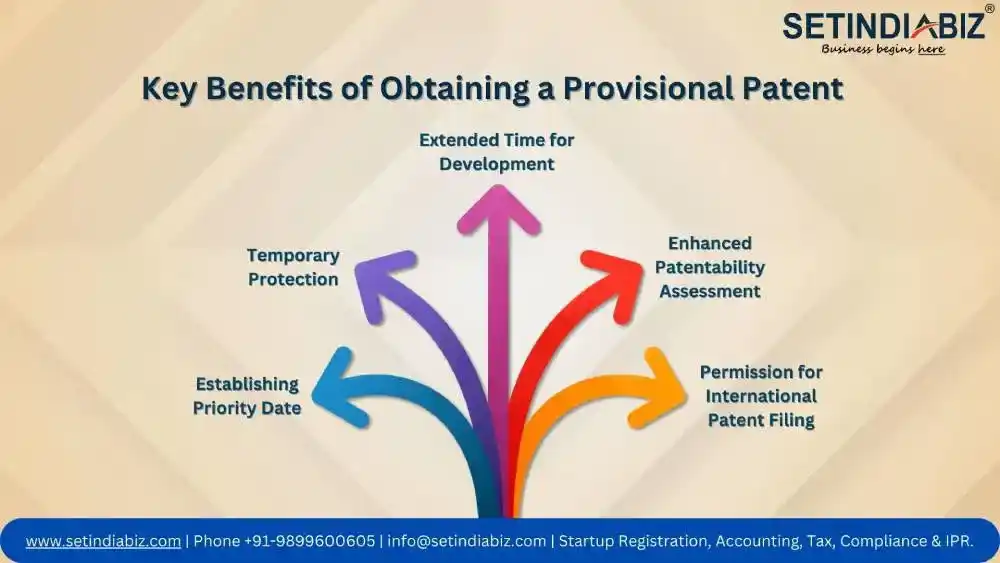
- Establishing Priority Date: A provisional application establishes an early priority date for the invention, providing the inventor with a competitive edge and ensuring priority rights over subsequent patent applications filed by others.
- Temporary Protection: A provisional patent offers temporary protection for the invention, allowing inventors to disclose their innovations to potential investors, partners, or licensees while maintaining confidentiality and preserving their intellectual property rights.
- Extended Time for Development: By securing a provisional patent, inventors gain an additional 12 months to further develop their inventions, conduct market research, and explore commercialization opportunities before filing a complete patent application.
- Enhanced Patentability Assessment: Provisional application enables inventors to assess the patentability of their inventions before committing to the full cost of filing a complete patent application. It provides valuable time to evaluate the novelty, inventiveness, and commercial potential of the invention.
- Permission for International Patent Filing: For inventors seeking international patent protection, a provisional patent can serve as the basis for filing corresponding patent applications in other countries under the Paris Convention or the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT), providing a streamlined and cost-effective approach to global patent protection.
Conclusion
The provisional patent filing process offers inventors a vital means of protecting their innovations during the proof of concept stage itself. This allows them enough time to develop their inventions without the fear of losing exclusive rights over them. By securing priority rights, gaining temporary protection, and allowing for extended time for development, provisional patents provide a cost-effective and flexible solution for safeguarding intellectual property. Understanding the importance of provisional patent application India is crucial for inventors looking to assert their rights and maintain a competitive advantage in the ever-evolving landscape of innovation.
FAQ's
Author Bio

Editorial Team | in
Setindiabiz Editorial Team is a multidisciplinary collective of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Advocates offering authoritative insights on India’s regulatory and business landscape. With decades of experience in compliance, taxation, and advisory, they empower entrepreneurs and enterprises to make informed decisions.
